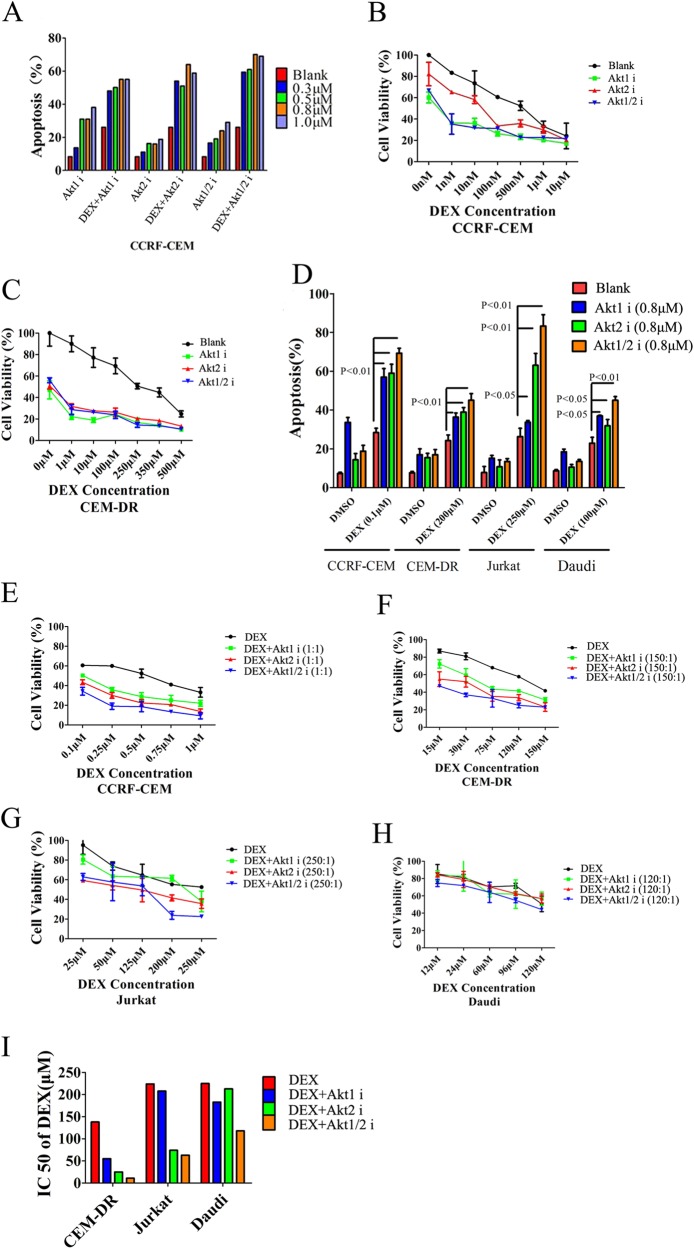
Fig. 5. Inhibition of Akt2 enhances sensitivity to GCs in T-cell tumors to a greater extent than inhibition of Akt1.
a Level of apoptosis in CCRF-CEM cells when cells were treated with DEX (0.1 µM), varying concentrations of the Akt1, Akt2, or Akt1/2 inhibitor (0.3, 0.5, 0.8, or 1 µM), or DEX combined with varying concentration of each of the Akt isoform inhibitors. b Quantification of cell viability of CCRF-CEM T-ALL cells treated with varying concentrations of DEX plus each of the Akt isoform inhibitors (0.8 µM). c Cell viability quantification in CEM-DR cells treated with different concentrations of DEX at indicated concentrations plus each of the Akt isoform inhibitors at a concentration of 0.8 µM. d Analysis of apoptosis in CCRF-CEM T-ALL cells, CEM-DR T-ALL cells, Jurkat T-ALL cells and Daudi Burkitt’s lymphoma cells treated with DEX, each of the Akt isoform inhibitors at 0.8 µM, or DEX combined with each of the Akt isoform inhibitors. e–h Cell viability quantification in CCRF-CEM cells, CEM-DR cells, Jurkat cells and Daudi cells treated with a fixed concentration ratio of DEX and each Akt isoform inhibitor. i IC50 of DEX in CEM-DR cells, Jurkat cells, and Daudi cells treated with DEX alone or DEX combined with the Akt1 inhibitor, Akt2 inhibitor or Akt1/2 inhibitor. Data in b, c, e–h show average measurements of triplicate biological replicas and error bars indicate ± SD. Bar graph in d represents mean ± SD