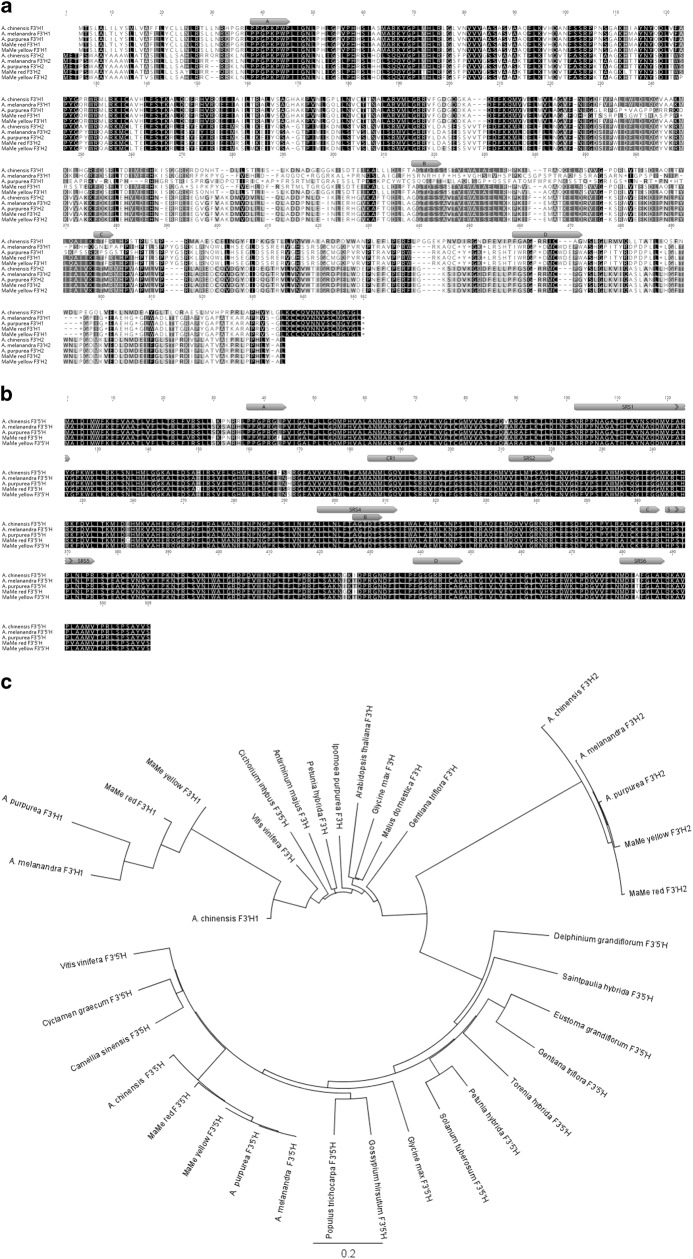
Fig. 3. Deduced amino acid sequences of Flavonoid 3′ Hydroxylases and Flavonoid 3′5′ Hydroxylases.
a Alignment of F3′H1 and F3′H2 from Actinidia chinensis, A. melanandra, A. arguta var. purpurea, MaMe Red and MaMe Yellow. The deduced amino acid sequences predicted multiple stop codons throughout the F3′H1 sequences except for the A. chinensis. b Alignment of F3′5′H sequences from the above mentioned species. Motifs specific to P450 enzymes are shown in both alignment A and B. Box A: proline-rich hinge region, box B: oxygen-binding pocket motif, box C: EXXR motif, box D: heme-binding domain. Substrate recognition sites (SRS) 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 and functional domains for hydroxylation activity (CR1) are labelled in F3′5′H amino acid alignment. c Phylogenetic relationship between F3′Hs and F3′5′Hs from kiwifruit and other plant species. Deduced amino acid sequences were aligned by global alignment with free end gaps. The protein distance was calculated by Jukes-Cantor model and the tree was constructed by neighbour-joining method using 1000 bootstrap replicates in Geneious 10.0.3