Figure 2.
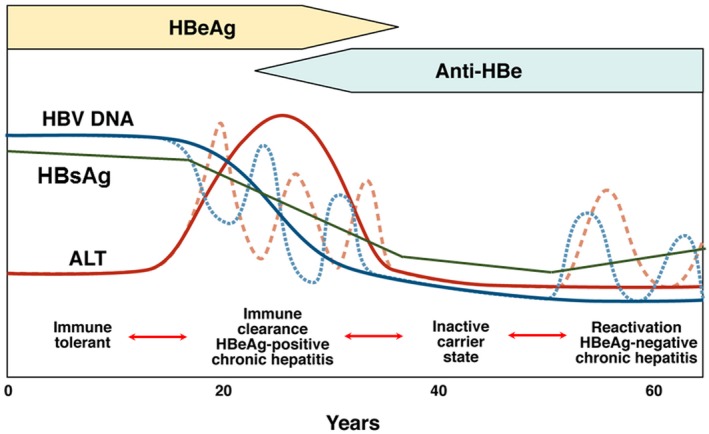
Phases of chronic HBV infection.3 Traditionally, phases of chronic HBV infection are defined by HBeAg status, serum HBV DNA, and ALT levels. Quantitative HBsAg levels are different in each phase and are generally highest in the immune tolerant phase and lowest in the inactive carrier phase. Although most patients progress from one phase to the next, not all patients go through each phase; reversion to an earlier phase can occur. Immune tolerant: HBeAg‐positive, high serum HBV DNA but normal ALT levels. Immune clearance/HBeAg‐positive chronic hepatitis: HBeAg‐positive, high serum HBV DNA, and elevated ALT levels; HBeAg seroconversion to anti‐HBe occurs after varying durations. Inactive carrier: HBeAg‐negative, serum HBV DNA low (generally <2,000 IU/mL) or undetectable. Reactivation/HBeAg‐negative chronic hepatitis: HBeAg‐negative, elevated levels of HBV DNA and ALT in serum, HBV precore and/or basal core promoter variant often present. Abbreviation: HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen.
