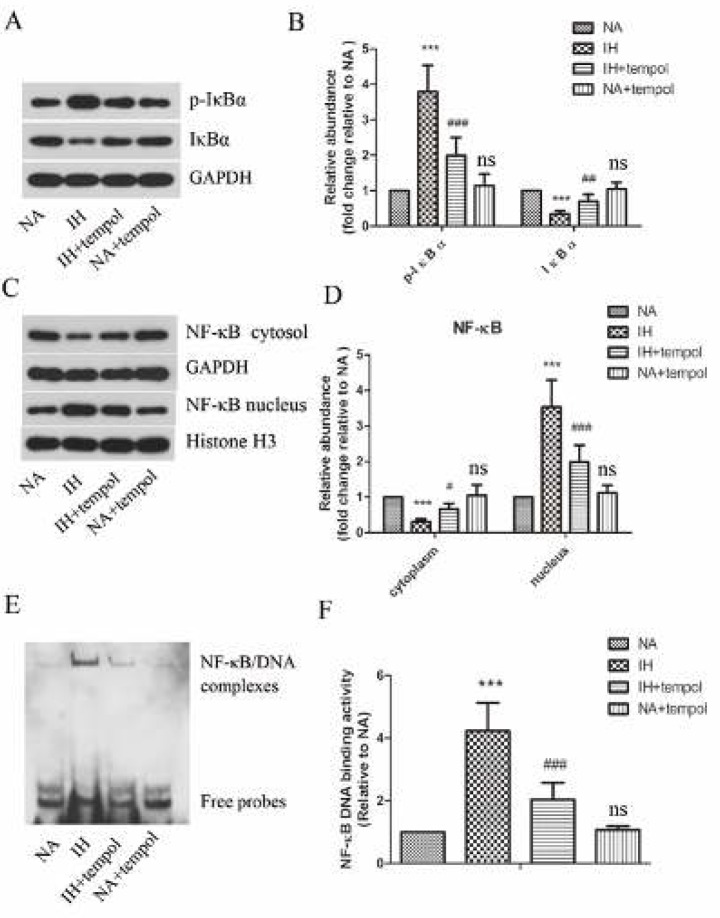
Figure 4.
Tempol inhibited intermittent hypoxia-induced activation of NF-κ B signaling pathway. (A)&(C) The protein levels of p-I κ B α, I κ B α, cytoplasmic NF-κ B, and nuclear NF-κ B were determined by Western blot assay. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B)&(D) The gray-scale value of the bands was quantitatively analyzed. (E) DNA binding activity of NF-κ B in lung tissues was assessed by EMSA. (F) Quantitative analysis of NF-κ B DNA binding activity. The experimental data were expressed as mean ± SD (n=6). *** P<0.001, versus the NA group. # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001, versus the IH group. ns, no significance, versus the NA group