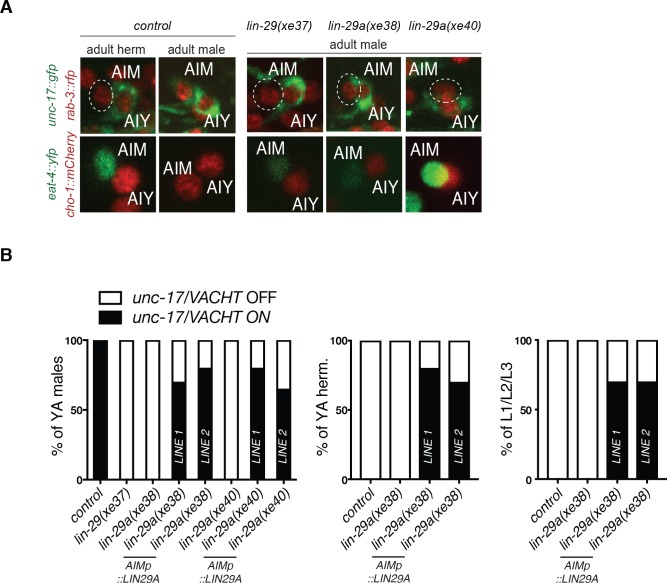
Figure 5. Cell-autonomy and sufficiency of lin-29a for the AIM neurotransmitter switch.
(A) The neurotransmitter switch is blocked in three newly generated lin-29 mutants. In adult control animals, the fosmid-based cholinergic reporters unc-17/VACHT (otIs576) and cho-1/CHT (otIs544) are expressed in AIM neurons of adult males but not hermaphrodites while the eat-4/VGLUT (otIs518) glutamatergic reporter is expressed in AIM neurons of adult hermaphrodites but not males. The AIM neurotransmitter switch is blocked in a newly generated lin-29a/b(xe37) null allele and in two lin-29a-specific mutants (xe38 and xe40). In these lin-29 mutant males, AIM fails to turn on cholinergic markers unc-17/VACHT (top panels) and cho-1/CHT (bottom panels) and expresses a pan neuronal maker rab-3::rfp (top panels) and the glutamatergic marker eat-4/VGLUT (bottom panels). A pan-neuronal rab-3::rfp (otIs355) reporter was used to label all neurons in the top panels. (B) AIM-specific LIN-29A expression is sufficient to cell-autonomously rescue the neurotransmitter switch in males and induce it in young larvae and the opposite sex. LIN-29A expression was driven under an AIM-specific promoter in lin-29a mutant animals: LIN-29A was expressed in lin-29a(xe38) (otEx7316 and otEx7317) and in lin-29a(xe40) (otEx7318 and otEx7319). Expression of cholinergic gene reporter unc-17/VACHT (otIs576) was examined to assay rescue and ectopic induction of the AIM neurotransmitter switch (n = 15).