FIGURE 3.
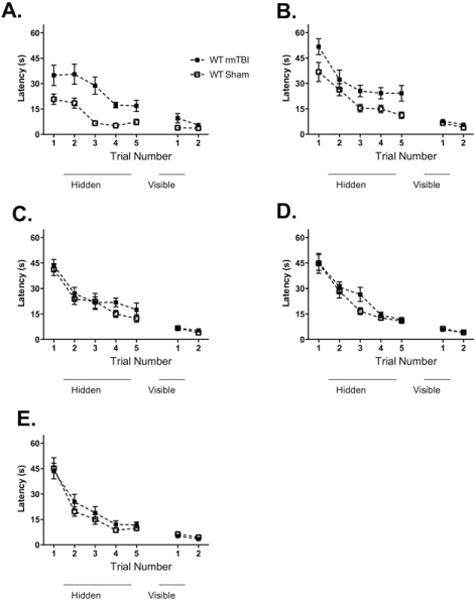
The effect of time interval between repetitive mild traumatic brain injuries (rmTBIs) on Morris water maze performance 6 months after the last injury. All groups demonstrated time-dependent improvement in hidden platform performance. There were no group differences in visual platform performance. Mice that underwent 5 concussive injuries in 5 days (A) and weekly concussive injuries for 5 weeks (B) had deficits in hidden platform performance when compared to sham-injured mice (n = 5–8/group, p = 0.001 and n = 11–16/group, p = 0.002, respectively). There were no differences in hidden platform performance between injured and sham-injured mice that underwent biweekly injuries for 10 weeks (n = 11–14, p = 0.1; C), 5 monthly injuries (n = 12–16/group, p = 0.2; D), or 1 injury (n = 11–15/group, p = 0.4; E). WT = wild type.
