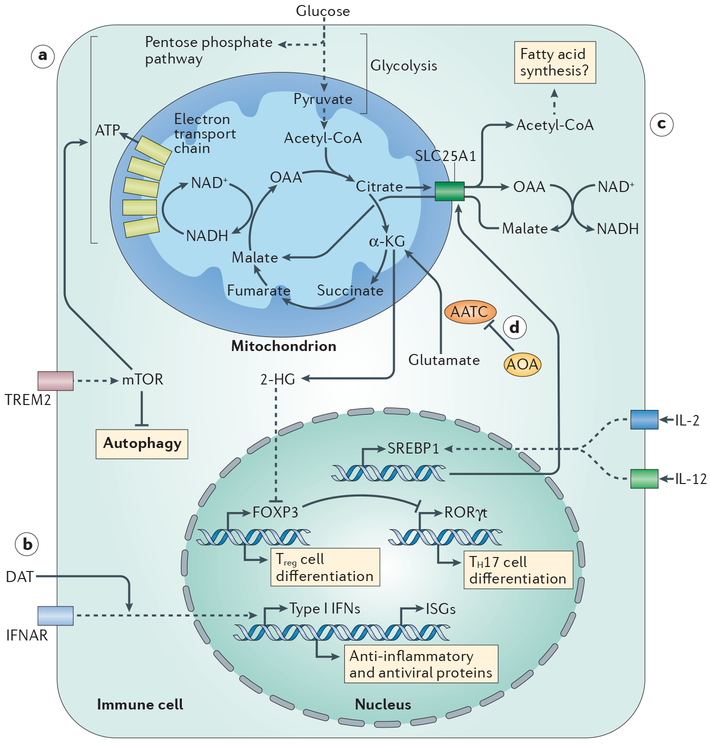
Figure 1 |. Metabolic programmes regulate immune cell function.
a | In microglia, signalling through triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) promotes activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), which balances anabolic metabolism and ATP production. b | Positive effects of the microbiota on influenza virus infection are mediated by the microbial metabolite desaminotyrosine (DAT), which potentiates signalling downstream of the type I interferon receptor (IFNAR). c | Metabolic support for natural killer (NK) cell activation by IL-2 and IL-12 is provided by induced expression of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP1), which upregulates expression of SLC25A1. This citrate–malate shuttle enables NADH to be moved into mitochondria, where it fuels ATP production. d | (Amino-oxy)acetic acid (AOA) limits T helper 17 (TH17) cell development by inhibiting the activity of aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic (AATC), which catalyses the conversion of glutamate into α-ketoglutarate (α-KG; the precursor of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)). 2-HG promotes the methylation and transcriptional inactivation of Foxp3. OAA, oxaloacetic acid.