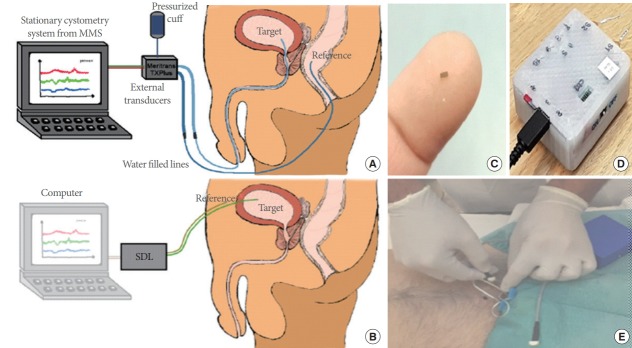
Fig. 1.
A new cystometry system using a microelectromechanical system (MEMS)-based in-target bladder pressure sensor. (A) Bladder pressures are usually measured from water-filled lines that are connected to externally located transducers. The conventional method uses a catheter through the urethra into the bladder with a transducer in the distal end. This method is implemented with nonphysiological filling state and urethra obstructed by a catheter and produce artefacts by movements and measurement errors. (B) The MEMS-based system is developed in a suprapubic approach to resolve the several limitations of conventional method. It consists of a MEMS sensor (C), custom-made sensor data logger (SDL) (D), and reference sensor probe. This in-target organ pressure sensor is superior in measuring minute pressure pulses. This method is improving the quality of measurements and the option of long-term implantable devices. (E) The clinical trial. MMS, medical measurements systems. Reprinted from Clausen I, et al. Sensors (Basel) 2018 Jul 3;18(7), according to Open Access [51].