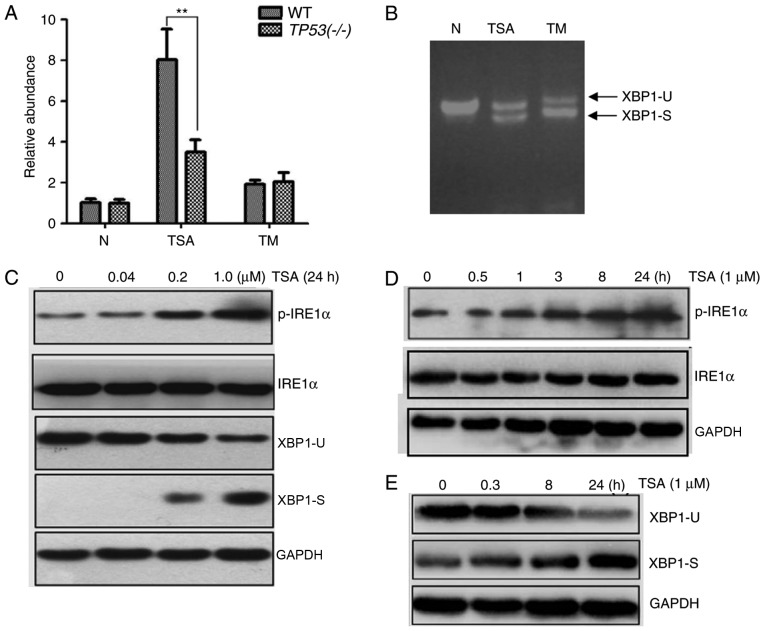
Figure 4.
Effect of TSA treatment on the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway. In the luciferase reporter assay, cells were transfected with pCAX-F-XBP1delDBD-Luc. (A) An increase in luciferase activity was associated with TSA and TM treatment at a concentration of 1 µM for 24 h. When treated with TSA the luciferase activity was significantly higher in WT HCT116 cells compared with HCT116 TP53(−/-) cells. (B) The spliced form of XBP1 was detected by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. (C) A decrease of XBP1-U and an increase of XBP1-S were associated with an increasing concentration of TSA. Similarly, an increase of p-IRE1α was associated with an increasing concentration of TSA. (D) An increase of p-IRE1α was associated with the treatment time of 1 µM TSA. (E) An increase of XBP1-S and a decrease of XBP1-U was associated with the treatment time of 1 µM TSA. **P<0.01. TSA, trichostatin A; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme 1 α; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1; TM, tunicamycin; WT, wild type; XBP1-U, unspliced XBP1; XBP1-S, spliced XBP1; p-IRE1α, phosphorylated IRE1α.