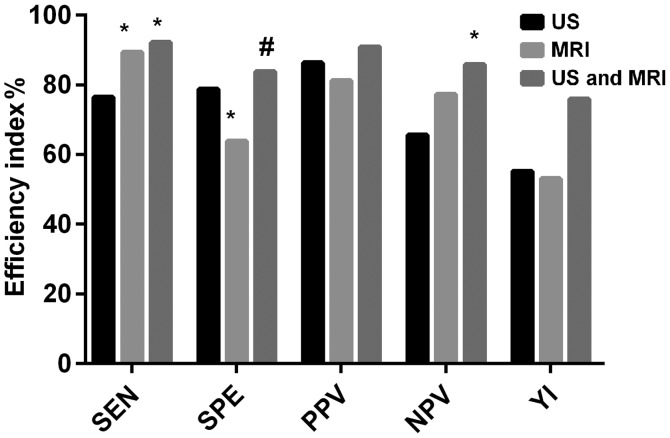
Figure 1.
The SEN of MRI alone was not different from that of US combined with MRI (P>0.05), but that of MRI alone and US combined with MRI was higher than that of US alone (P<0.05). The SPE of US alone was not different from that of US combined with MRI (P>0.05), but that of MRI alone was lower than that of US alone and US combined with MRI (P<0.05). The difference in the PPV among three methods was not statistically significant (P>0.05). The NPV of US alone and US combined with MRI was not different from that of MRI alone (P>0.05). The NPV of US combined with MRI was significantly higher than that of US alone (P<0.05). The YI of US combined with MRI was significantly higher than that of US alone and MRI alone, and that of US alone was not significantly different from that of MRI alone. *P<0.05, with the same diagnostic efficacy indicator, compared with US; #P<0.05, with the same diagnostic efficacy indicator, compared with MRI.