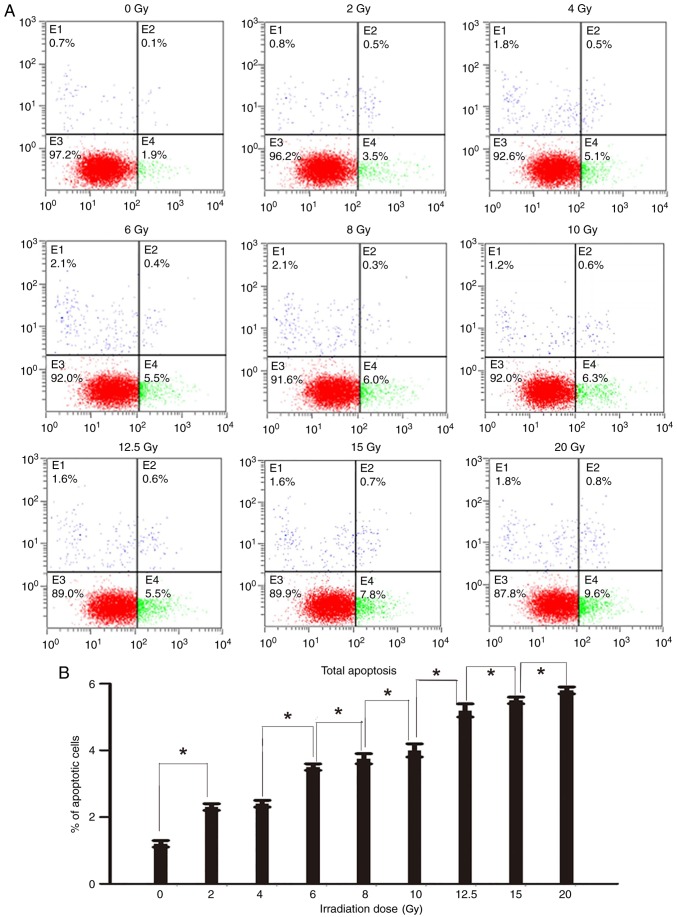
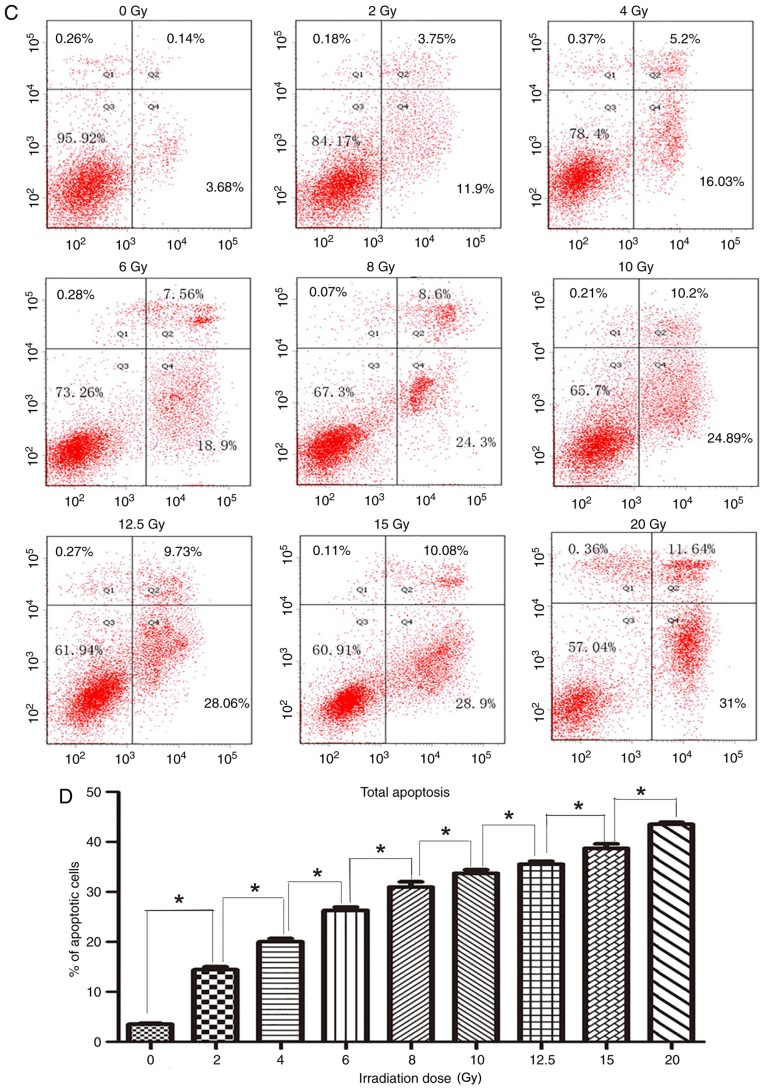
Figure 5.
Apoptosis of cells following irradiation. (A) The apoptotic cells at 48 h after irradiation, stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, were analyzed using a flow cytometer. Cells were classified into 4 subpopulations as follows: Viable cells (lower left), early apoptotic cells (lower right), cell fragments and damaged cells (upper left), and late apoptotic cells (upper right). (B) The percentage of apoptotic cells at 48 h after irradiation with different irradiation doses (lower right and upper right). The radio of apoptotic cells of two groups with adjacent doses were compared with each other. Except 2 and 4 Gy groups (difference between the 2 and 4 Gy groups was not significant), the difference in the percentage of apoptotic cells between other adjacent two groups were significant *P<0.05. (C) The apoptotic cells at 72 h after irradiation, stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, were analyzed using a flow cytometer. Cells were classified into 4 subpopulations as follows: Viable cells (lower left), early apoptotic cells (lower right), cell fragments and damaged cells (upper left), and late apoptotic cells (upper right). (D) The percentage of apoptotic cells at 72 h after irradiation with different irradiation doses (lower right and upper right). The radio of apoptotic cells of two groups with adjacent doses were compared with each other. Except 2 and 4 Gy groups (difference between the 2 and 4 Gy groups was not significant), the difference in the percentage of apoptotic cells between other adjacent two groups were significant *P<0.05. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PI, propidium iodide.