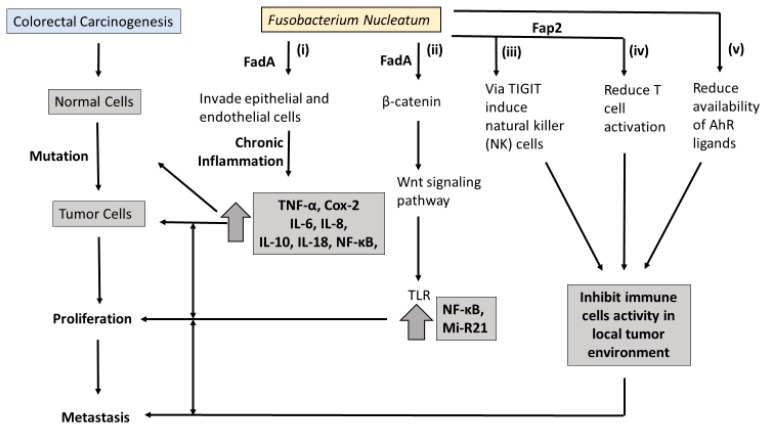
Figure 1.
Summary of five hypothetical pathways of Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) in promoting colorectal carcinogenesis: (i) FadA in Fn promotes chronic Fn infection of colon mucosa that triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS) and proinflammtory mediators; (ii) Fad2 activates β- catenin signaling that, through the Wnt signaling pathway, results in increased miRNA and NF-κB, and ultimately increases tumor proliferation; (iii) Fap2 interacts with TIGIT on natural killer (NK) and T cells to suppress immune response and promote tumor growth; (iv) Fn through Fap2 may recruit tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells; (v) Fn in conjunction with other microbiota may affect the production of Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligands. AhR mediates the transcription of cytokines that regulate immune response and immune-response inhibition promotes tumor growth.