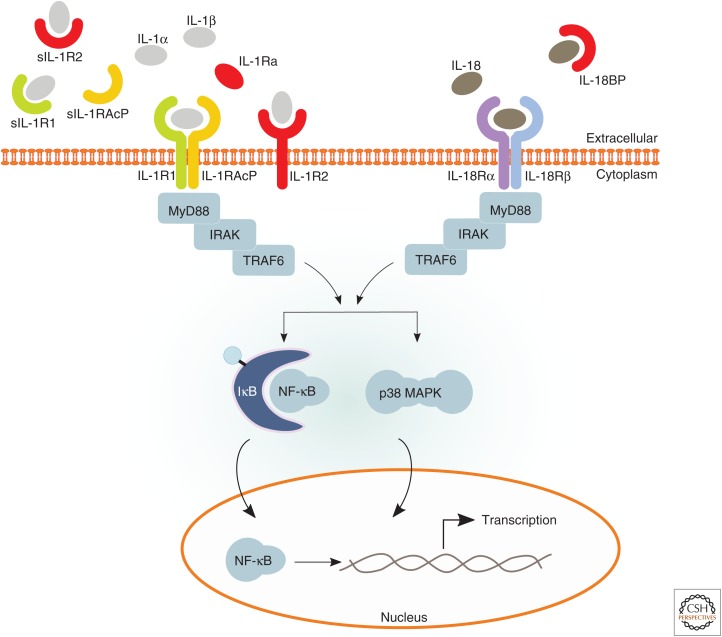
Figure 1.
Interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, and IL-18 receptor complexes and downstream signaling. Pro-IL-1α, mature IL-1α, and mature IL-1β can all bind to IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1), which enables recruitment of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) coreceptor. Approximation of the intracellular Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domains of the IL-1R complex results in recruitment of MyD88 followed by a cascade of downstream events that ultimately result in the activation of important signaling proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs, e.g., p38), as well as transcription factors, including nuclear factor (NF)-κB, which control expression of a number of inflammatory genes. Signaling through the IL-1R complex is modulated by inhibitory actions of membrane-bound IL-1R2, soluble IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), and soluble forms of the receptors (sIL-1R1, sIL-1R2, and sIL-1RAcP). On binding of IL-18 to IL-18Rα, IL-18Rβ then is recruited to the complex. Similar to the IL-1R complex, approximation of the two receptors results in recruitment of MyD88 and a downstream cascade activating signaling proteins and transcription factors. Signaling through the IL-18R complex is modulated by inhibitory actions of IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP).