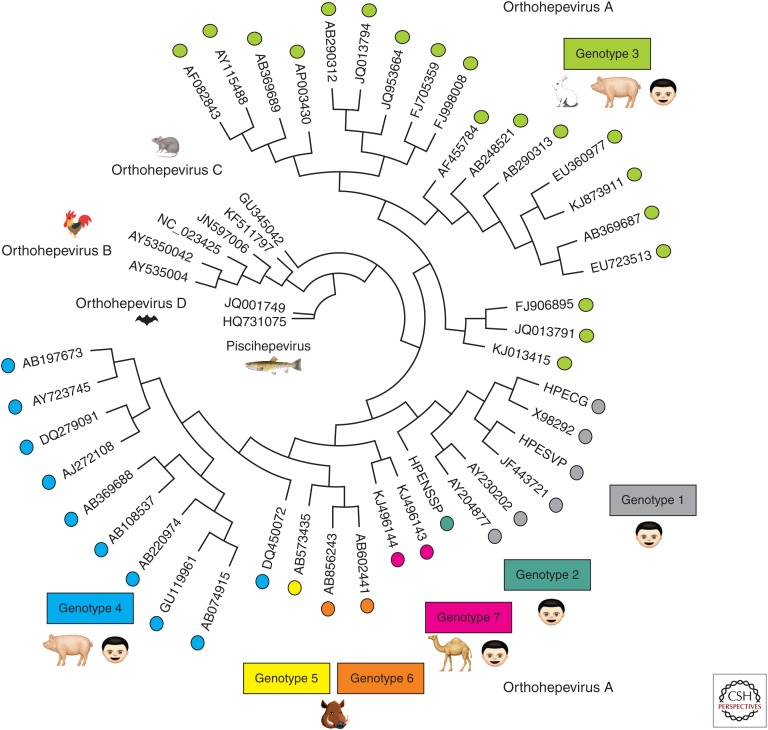
Figure 1.
A phylogenetic tree encompassing all of the newly International Committee for Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)–recognized reference strains of the family Hepeviridae. All recently proposed reference strains for hepatitis E virus (HEV) (Smith et al. 2014, 2016) were aligned and placed into a circular phylogenetic tree using Geneious software v10.2.2 by Biomatters (see geneious.com). Sequence alignment parameters included global alignment with free end gaps with a cost matrix of 65% similarity. The tree was generated using the Tamura-Nei genetic distance model with a neighbor joining tree build method. The more divergent strains of HEV are located toward the center (Piscihepevirus) and the more conserved strains are located around the circumference (Orthohepevirus A strains). The Orthohepevirus A strains are color-coded to match their respective genotype. Cartoons depict which host species the viruses are known to infect. Orthohepevirus C are also able to infect ferrets, mink, Asian musk shrew, and greater bandicoot (Smith et al. 2014). Orthohepevirus B are reported to infect turkeys, little egrets (Reuter et al. 2016), and wild birds (Zhang et al. 2017).