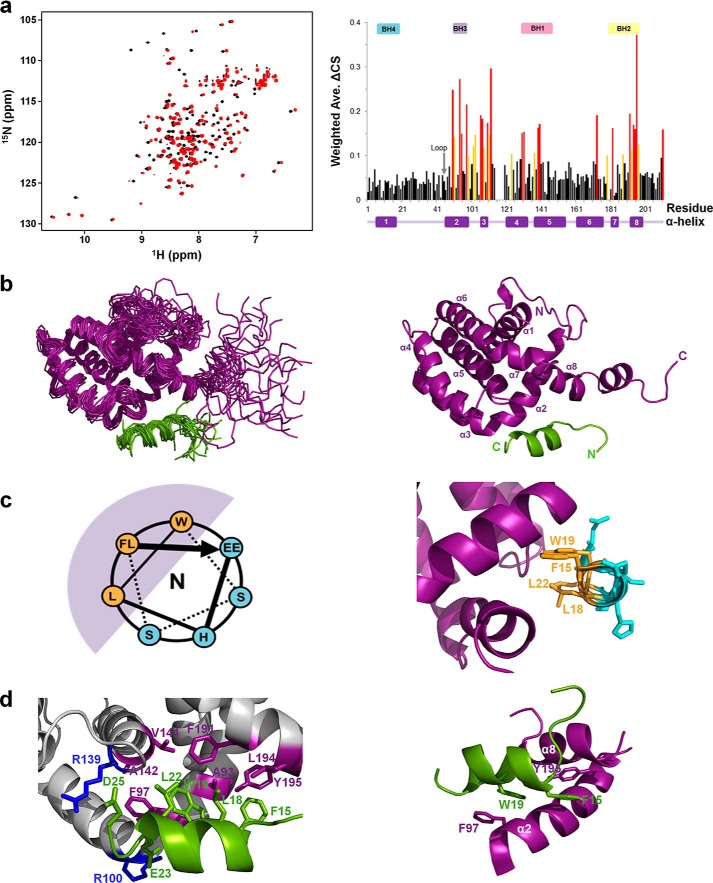
Figure 4.
Solution structure of the Bcl-XL–p73-TAD16 peptide complex. a, the overlaid 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra for 15N-labeled Bcl-XL in the absence (black) or presence (red) of the p73-TAD16 peptide (left panel). The Bcl-XL residues showing chemical shift changes of ΔCS > 0.15 ppm and 0.1 ppm < ΔCS < 0.15 ppm are colored red and yellow, respectively (right panel). The α-helices and BH domains are indicated in the bottom and top of the graph, respectively. b, the ensemble of the final 20 lowest-energy NMR structures of the Bcl-XL–p73-TAD16 peptide complex (left) and a representative structure (right). The Bcl-XL and p73-TAD16 peptide are colored purple and light green, respectively. c, the helical wheel diagram of the p73-TAD16 peptide bound to Bcl-XL (left) and the corresponding region in the structure (right). The view is from the N terminus. The helical region of the p73-TAD16 peptide, encompassing residues Phe15–Glu23, is shown. The bulky hydrophobic residues in the p73-TAD16 peptide (Phe15, Leu18, Trp19, and Leu22) (orange) face the hydrophobic groove of Bcl-XL (purple), whereas the remaining hydrophilic residues (cyan) are exposed to the solvent. d, the binding interface between the Bcl-XL and p73-TAD16 peptide. The p73-TAD16 residues involved in the interactions with Bcl-XL are shown in green, and the Bcl-XL residues that are involved in the hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions with the p73-TAD16 peptide are shown in purple and blue, respectively (left panel). The two intermolecular π-stacking interactions between Phe97 and Tyr195 in Bcl-XL and Trp19 and Phe15 in the p73-TAD16 peptide, respectively, are shown (right panel). Ave., average.