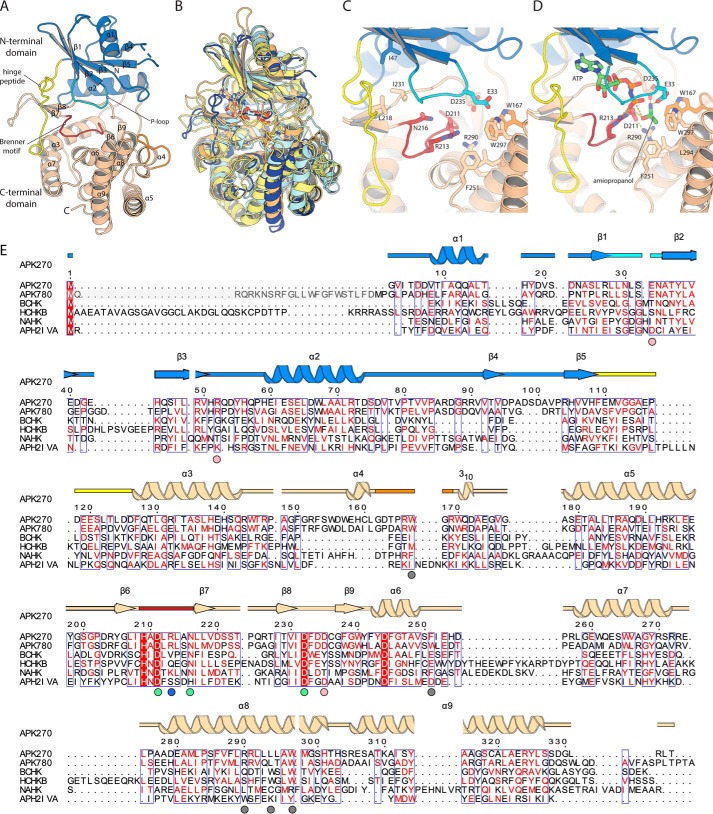
Figure 2.
Structure of APKMSM270. A, structure of the APKMSM0270 monomer. Secondary structure elements are labeled. B, superposition of APKMSM0270 with representative structural homologs. APKMSM0270 is shown in dark blue. N-Acetylhexosamine-1-phosphate kinase (PDB 4ocq) is shown in pale yellow. Choline kinase (PDB 4r78) in pale orange. Spectinomycin phosphotransferase (PDB 3i0o) is shown in pale cyan. C, details of the catalytic site of APKMSM0270. D, model of the ternary complex of APKMSM0270 with ATP and propanolamine. E, multiple sequence alignment of APK with structural homologs. The secondary structure is colored as described in A. APKMSM0270 is aligned with APKMSM0780 (greyed residues are present in UniProt but are likely a misannotation), S. pneumoniae bacterial choline kinase (BCHK, UniProt Q8DPI4), Homo sapiens choline kinase B (HCHKB, UniProt Q9Y259), B. longum N-acetylhexosamine 1-kinase (NAHK, UniProt E8MF12), and Enterococcus casseliflavus aminoglycoside phosphotransferase (2′)-Iva. The secondary structure and residue numbering of APKMSM0270 are aligned with the multiple sequence alignment. Colored circles below the multiple sequence alignment indicate residues of the hydrophobic methyl binding pocket (gray), substrate α-amino binding (pink), conserved Brenner motif (green), and the phosphate-product stabilizing residue (light blue).