Fig. 1.
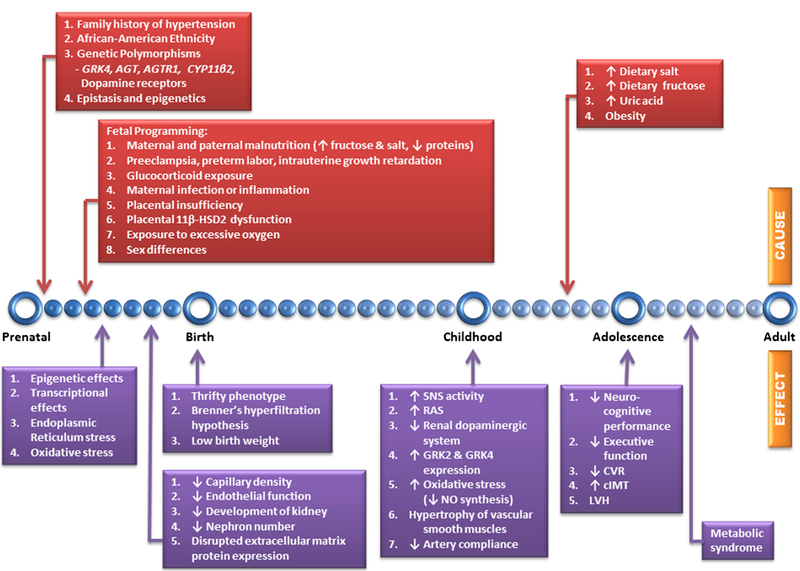
Timeline showing the pathogenesis of pediatric hypertension. Identified underlying causes and short-term and long-term effects are shown above and below the blue line, respectively. Genetic predisposition, early developmental insults, and dietary influences lead to changes in the regulation of BP that are carried into adulthood. GRK4 G protein-coupled receptor kinase type 4, GRK2 G protein-coupled receptor kinase type 2, AGT angiotensinogen gene, AGTR1 angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 receptor gene, CYP11β2 aldosterone synthase gene, ↑ increase, ↓ decrease, 11β-HSD2 placental 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2, SNS sympathetic nervous system, RAS Renin-angiotensin system, NO nitric oxide, CVR cerebrovascular reactivity, cIMT carotid intimal-medial thickness, LVH left ventricular hypertrophy
