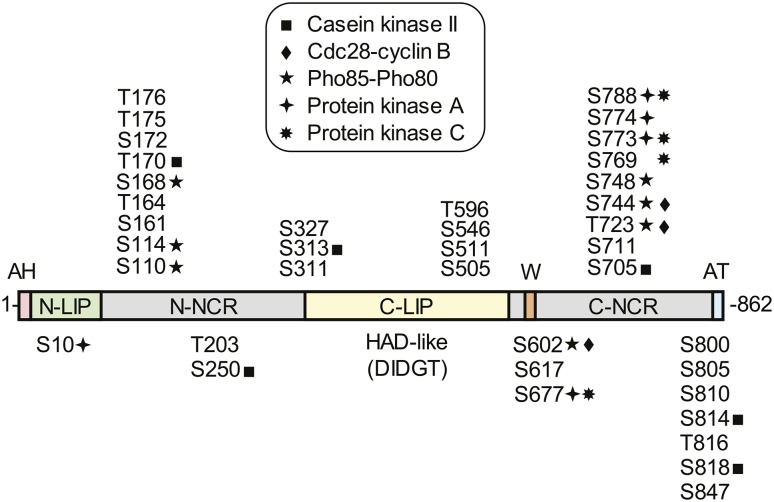
Fig. 2.
Domains/regions and phosphorylation sites in Pah1. The diagram shows the positions of the amphipathic helix (AH, pink) required for ER membrane interaction, the N-LIP (green) and C-LIP (contains HAD-like domain with DIDGT catalytic motif) (yellow) domains that are required for PA phosphatase activity, the acidic tail (AT, blue) required for interaction with Spo7 of the Pah1 phosphatase, N-terminal non-conserved region (N-NCR, grey), C-terminal non-conserved region (C-NCR, grey), the serine (S) and threonine (T) residues in their approximate regions that are known phosphorylation sites, and the sites that are phosphorylated by CKII, Cdc28-cyclin B, Pho85-Pho80, PKA, and PKC, and the tryptophan (W) residue within the C-terminal conserved sequence WRDPLVDID (orange) required for Pah1 function in vivo.