Figure 8.
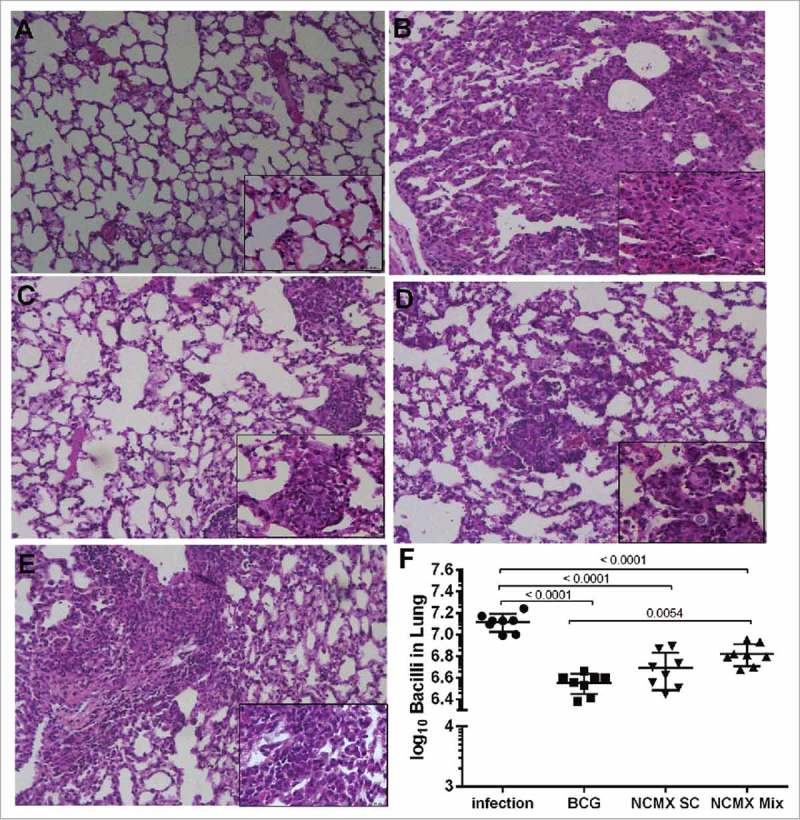
Vaccination with NCMX reduced the histopathological damage and bacterial load in the lungs of Mtb-challenged mice. Thirty days after the last vaccination via subcutaneous and mixed administration, mice were challenged with 106 CFU per animal. After thirty days, the mice were euthanized, and the lungs were studied to determine the capacity of the vaccination to protect against damage and pathological response (A to E), as well as its capacity to diminish the bacterial load in the lungs (F). Lung samples were also stained with H&E and analyzed for damage at 4x magnification and 40x magnification. Differences among the mean CFU values were determined by one-way ANOVA, and p values are shown. Significant differences were demonstrated among the groups, n = 8.
