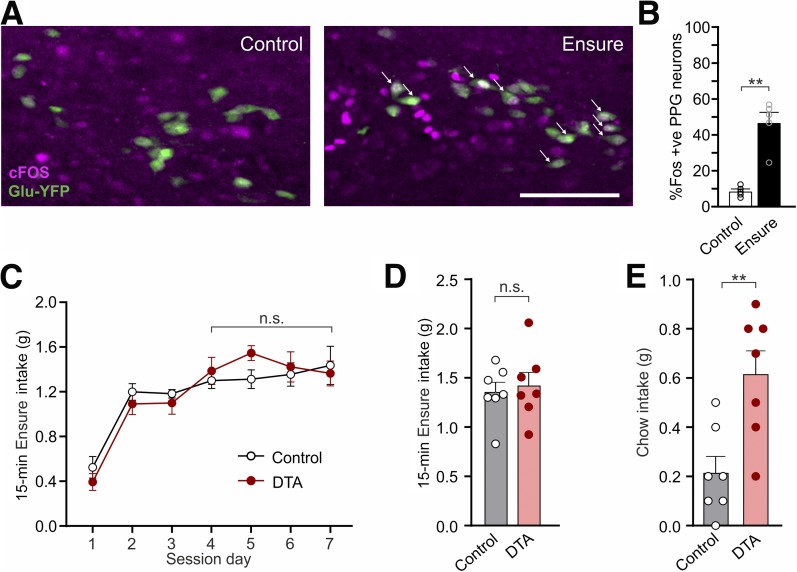
Figure 6.
Intake of large volumes of highly palatable diet activates PPG neurons. A: Expression of the immediate early gene cFOS (green) in PPG neurons after 30 min access to Vanilla Ensure or no access to food (control). White arrows: representative cFOS-positive PPG neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. B: Percentage of PPG neurons expressing cFOS 90 min after 30-min access to Vanilla Ensure or no access to food. Data are given as the mean ± SEM; n = 3 (control), n = 3 (Ensure). P = 0.0079 (Mann-Whitney U test). C: Ensure intake during 15-min access at dark onset over several days of habituation in control and PPG-ablated (DTA) mice. Data are given as the mean ± SEM; n = 7 (control), n = 7 (DTA). No interaction of virus × time (F(3,36) = 0.592, P = 0.62) and no significant main effect of virus (F(1,12) = 1.135, P = 0.31) or time (F(3,36) = 0.19, P = 0.90).). D: Ensure intake during the 15-min access period on the test day in control and PPG-ablated (DTA) mice. Data are given as the mean ± SEM; n = 7 (control), n = 7 (DTA). P = 0.70 (unpaired t test). E: Chow intake of control and PPG-ablated (DTA) mice for 1 h after 15-min access to Vanilla Ensure. Data given as the mean ± SEM; n = 7 (control), n = 7 (DTA). P = 0.0052 (unpaired t test). **P < 0.01. n.s., not significant.