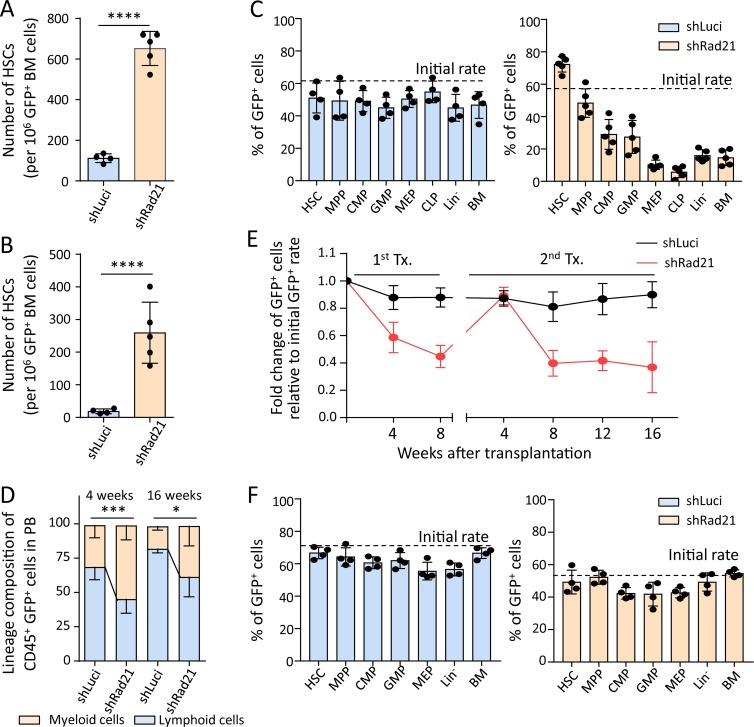
Figure 3.
Rad21 deficiency increases self-renewal and leads to impaired and myeloid-skewed differentiation of HSPCs. (A–D) Freshly isolated LSK cells were infected with an shRNA against Rad21 shRad21 or a control virus (shLuci) in culture and transplanted into lethally irradiated mice together with noninfected LSK cells from the same culture. (A and B) The number of HSCs (GFP+CD150+CD34−LSK cells) derived from infected LSK cells in the primary recipients (A) and the secondary recipients (B) that were transplanted with total BM cells of the primary recipients at 4 mo after the first transplantation. The dots represent individual recipient mice (n = 4–5 mice per group per experiment, n = 3 independent experiments, one of the three repeat experiments is shown, the other experiments showed similar results). Statistical values were calculated by Welch’s t test after log transformation. (C) The chimerism of GFP+ cells from the primary recipients was analyzed by FACS at 4 mo after transplantation in the indicated populations. HSC: CD150+CD34−LSK; MPP: CD34+LSK; CMP: common myeloid progenitor (Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1−CD34+FcγR−); GMP: granulocyte macrophage progenitor (Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1−CD34+FcγR+); MEP: megakaryocyte erythrocyte progenitor (Lin−c-Kit+Sca-1−CD34−FcγR−), CLP: common lymphoid progenitor (Lin−c-KitlowSca-1lowIL-7Ra+Flt3+), Lin−: lineage− cells; BM: total BM cells. n = 4–5 mice per group per experiment, three independent experiments, one of the three experiments is shown, the other experiments showed similar results. (D) PB cells from the primary recipients were analyzed by FACS. The histogram shows the percentage of myeloid and lymphoid cells in GFP+CD45+ cells in the PB at the indicated time points after transplantation (n = 4–5 mice per group for each experiment, n = 3 independent experiments, one of the three experiments is shown; the other experiments showed similar results). Statistical significance for myeloid cells was assessed by Welch’s t test after logit transformation of the data. (E and F) LSK cells from young (2 mo old) wild-type mice were transduced with shLuci or shRad21 virus followed by transplantation into 2–3-mo-old recipients. 8 wk after transplantation, recipient mice were sacrificed and total BM was transplanted into secondary recipients. 4 wk after secondary transplantation, BM cells were analyzed to investigate the chimerism of shLuci- or shRad21-LSK cells in BM. Chimerism of shLuci- or shRad21-infected LSK cells in PB was monitored every 4 wk after each round of transplantation. (E) The data show the relative change of GFP+ cells in PB from the recipients at indicated time points after transplantation. The initial transduction efficiency was 71% for shLuci-LSK and 54% for shRad21-LSK (n = 5 recipient mice per group, per experiment in the primary transplantation, n = 10 recipient mice per group, per experiment in the secondary transplantation, n = 2 independent experiments, one of the two experiments is shown; the other experiment showed a similar result). (F) The histograms depict the chimerism of GFP+ cells in the indicated populations of the secondary recipients at 4 wk after transplantation. The dots represent individual mice (n = 4 mice per group for each experiment, n = 2 independent experiments, one of the two experiments is shown, the other experiment showed a similar result). Data in all panels of this figure depict mean ± SD; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.