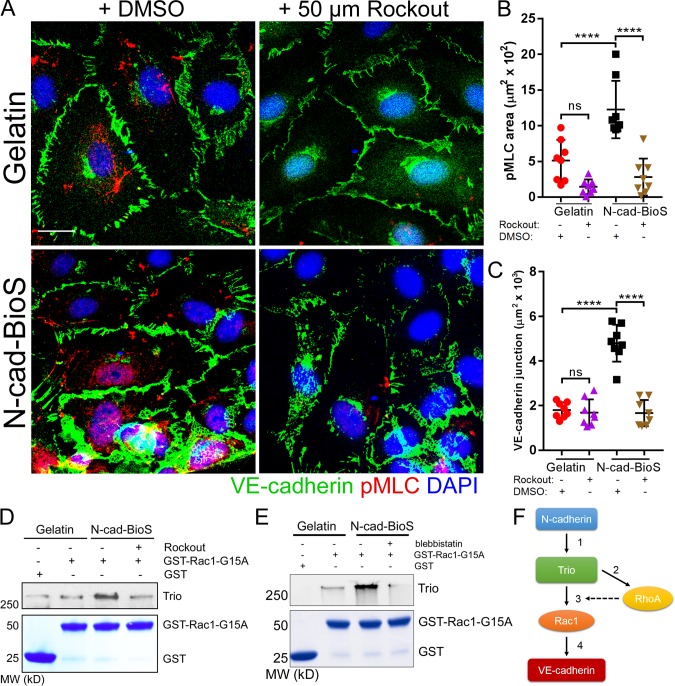
Figure 9.
N-cadherin interaction with Trio increases intracellular tension and reinforces Rac1 activation and promotes assembly of VE-cadherin junctions. (A) Confocal images of HPAECs grown on either gelatin or N-cad-BioS and treated with 50 µM Rockout to inhibit Rho kinase (ROCK) or vehicle (DMSO). Cells were stained for VE-cadherin (green), phosphorylated myosin light chain (pMLC, red) and nuclei (DAPI, blue). Bar, 10 µm. (B and C) Quantification of phospho-MLC (B) and VE-cadherin junction area (C) from images in A. Inhibition of ROCK significantly reduced the area of VE-cadherin adhesion only in cells grown on N-cad-BioS. n = 8 images per group from three independent experiments. ****, P < 0.0001, ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. Data are shown as mean ± SD. (D) Analysis of Trio activity. Pulldown of Trio with GST and GST-Rac1(G15A) from HPAECs grown on gelatin and N-cad-BioS platforms after treatment with DMSO (vehicle) or 50 µM Rockout for 10 min. The precipitates were probed for Trio. Treatment with Rockout reduced Trio interaction with Rac1. 5% Coomassie-stained proteins used for pulldown. (E) Analysis of Trio activity. Pulldown of Trio with GST and GST-Rac1(G15A) from HPAECs grown on gelatin and N-cad-BioS platforms after treatment with DMSO (vehicle) or for 50 µM blebbistatin for 10 min. The precipitates were probed for Trio. Treatment with blebbistatin reduced Trio interaction with Rac1. 5% Coomassie-stained proteins used for pulldown. (F) The circuit describing the role of N-cadherin adhesion-mediated signaling in assembling of VE-cadherin junctions through Trio-mediated activation of both Rac1 and RhoA. (1) N-cadherin forms a complex with Trio; (2) Trio activates RhoA increasing intracellular tension; (3) increased tension activates the Trio GEF1 domain toward Rac1; and (4) Rac1 increases VE-cadherin recruitment to AJs, whereas RhoA reinforces Rac1-mediated assembly of AJs.