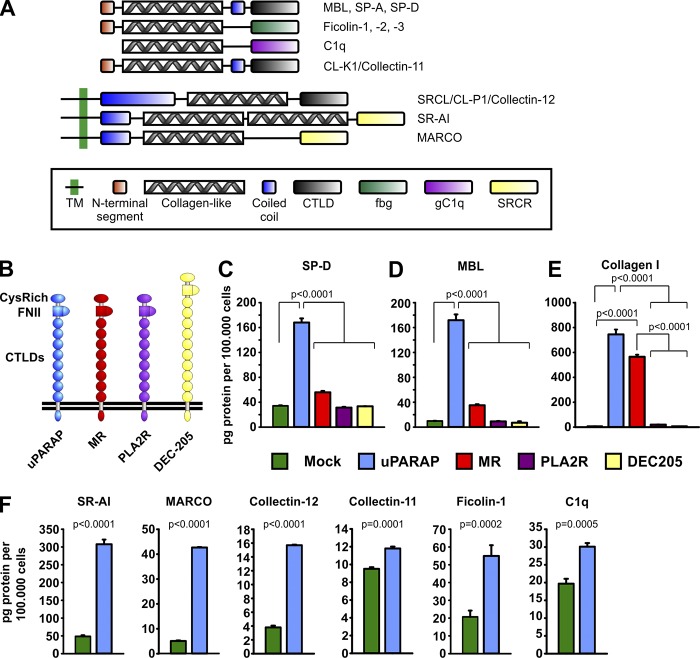
Figure 1.
uPARAP-dependent endocytosis of SP-D in vitro. (A) Domain structure of monomeric defense collagens SP-D, SP-A, MBL, ficolins, C1q, collectin-11, collectin-12, SR-AI, and MARCO. The domain structures include a collagen-like domain, which takes part in both homotypic and heterotypic protein interactions. TM, transmembrane domain; CTLD, C-type lectin-like domain; FBG, fibrinogen-like domain; gC1q, globular C1q domain; SRCR, scavenger receptor (SR) cysteine-rich domain. (B) Domain structure of the members of the MR protein family: uPARAP (ENDO180, MRC2, and CD280), MR (MRC1 and CD206), PLA2R (phospholipase A2 receptor), and DEC-205 (CD205). CysRich, cysteine-rich domain; FNII, fibronectin type-II domain. (C–E) Internalization of radiolabeled SP-D (C), MBL (D), and collagen type I (E) in CHO cells transfected to express uPARAP, MR, PLA2R, or DEC-205 or transfected with empty vector (mock). (F) Internalization of radiolabeled SR-AI, MARCO, collectin-12, collectin-11, ficolin-1, and C1q in CHO cells transfected to express uPARAP or mock cells. The following statistical tests were used: one-way ANOVA (C–E) and two-tailed Student’s t test (F). Analysis was performed in triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± SD.