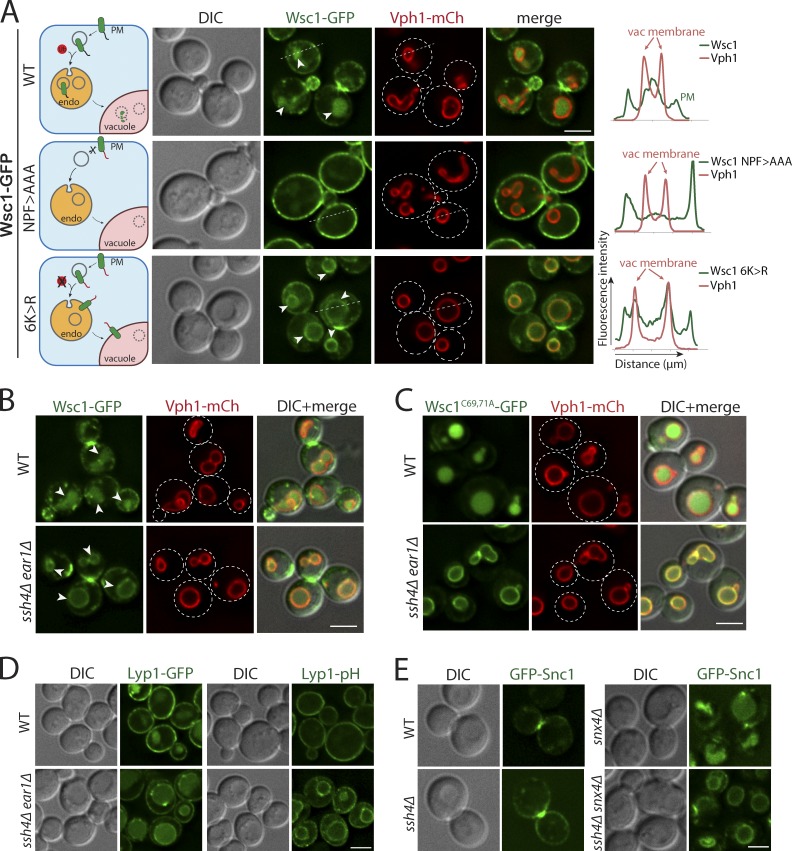
Figure 1.
Intracellular Rsp5 adaptors are required for vacuolar sorting of multiple endocytosed PM cargos. (A) Live-cell fluorescence and differential interference contrast (DIC) imaging of a GFP-tagged cell wall integrity sensor, Wsc1, and mutants lacking the Sla1 recognition motif (NPF>AAA) or all cytosolic lysines (6K>R) in WT yeast cells also expressing an mCherry-tagged VM marker, Vph1, a subunit of the vacuolar ATPase V0 domain. The arrowheads point to the vacuolar lumen signal for WT Wsc1 and the VM signal for Wsc16K>R mutant, respectively. The dashed line indicated on a representative cell for each condition was used to build a line-scan fluorescence profile using ImageJ. Schematic describing the localization phenotype for each condition is illustrated on the left. (B) WT and ssh4Δ ear1Δ mutant cells expressing Wsc1-GFP. The arrowheads point to the vacuolar lumen signal in WT cells and the VM signal in ssh4Δ ear1Δ mutant, respectively. (C) WT or ssh4Δ ear1Δ mutant yeast cells expressing clustering defective, constitutively endocytosed Wsc1C69, 71A-GFP. (D) WT or ssh4Δ ear1Δ double-mutant yeast cells expressing Lyp1 fused to GFP (Lyp1-GFP) or a pH-sensitive pHluorin (Lyp1-pHluorin). (E) Fluorescence microscopy of GFP-tagged v-SNARE Snc1 in WT, ssh4Δ, snx4Δ single mutants and ssh4Δ snx4Δ double mutant. Scale bars: 2.5 µm.