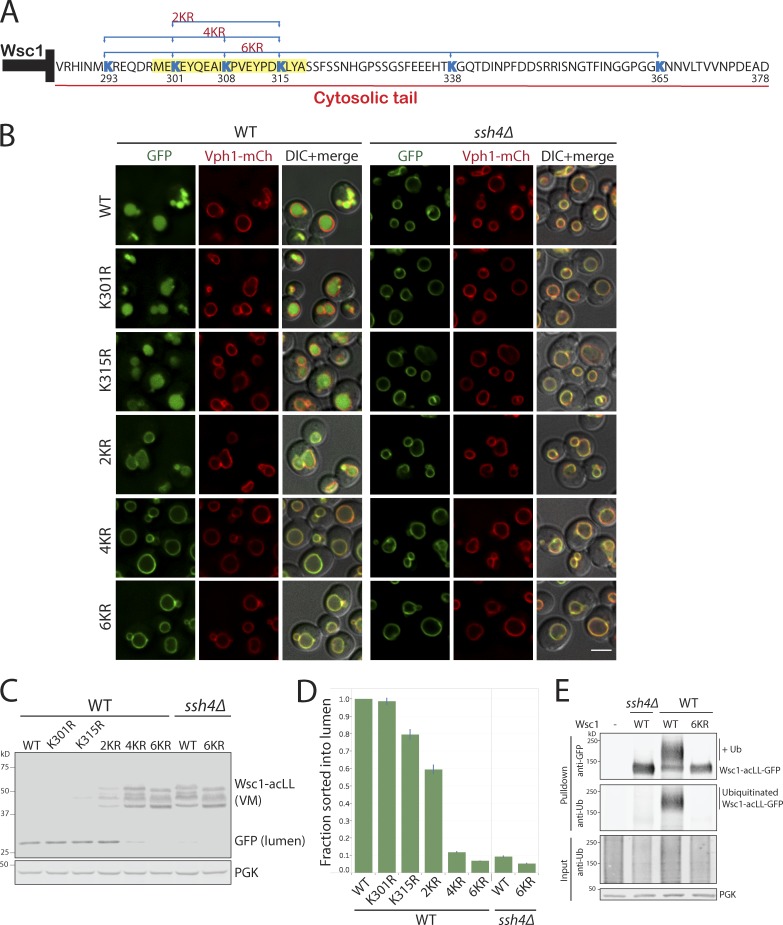
Figure 5.
The Ssh4–Rsp5 complex can target multiple accessible cytosolic lysines. (A) Sequence of the 93-aa cytosolic tail of Wsc1 with the lysines highlighted in blue. The position of the lysine residues and the combination mutants are indicated below and above the sequence, respectively. The 20-aa sequence in the Wsc1286–318 mutant required for sorting is highlighted in yellow. (B) WT and ssh4Δ mutant expressing Wsc1-acLL-GFP with K>R mutation at single (K301 or K315) or simultaneous mutations at two (2KR; K301R and K315R), four (4KR; K293R, K301R, K308R, and K315R), or all six (6KR; K293R, K301R, K308R, K315R, K338R, and K365R) cytosolic lysines. Scale bar: 2.5 µm. VM marker, Vph1-mCherry. (C) Immunoblot analysis on WT and ssh4Δ extracts expressing the mutants described in B. (D) Quantitation of three replicates of immunoblot analyses described in C. The fraction of Wsc1-acLL-GFP sorted into the lumen refers to the ratio of the processed GFP to the total reporter levels normalized to WT. Error bars indicate standard error of the measurements. (E) Immunoprecipitation followed by Western blot analysis of cells expressing WT or Wsc16K>R-acLL-GFP in WT or ssh4Δ cells (also lacking Doa4, Pep4, and Prb1 to stabilize ubiquitinated species).