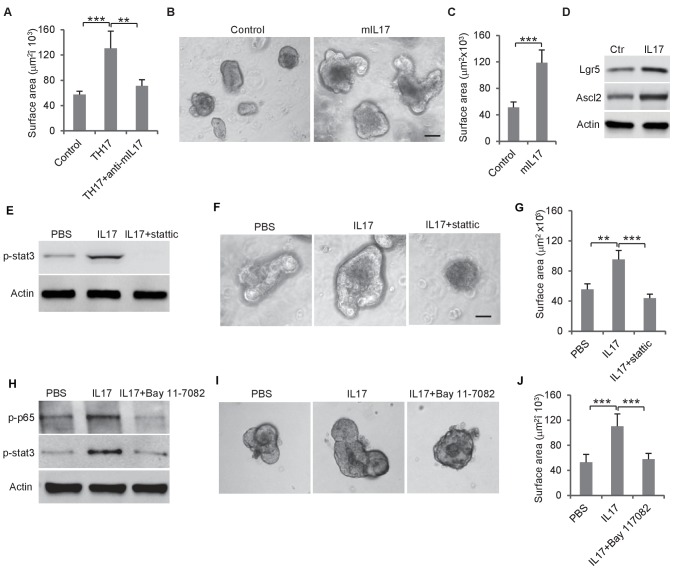
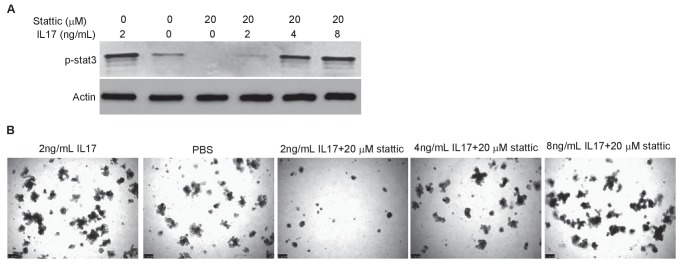
Figure 4. Th17 cells enhance colon organoid growth through IL-17.
(A) Th17 cells enhance colon organoid growth in co-culture. When co-cultured with Th17 cells, colon organoids grow faster with bigger surface area. Anti-IL-17 antibody abrogates Th17 promotion of colon organoids growth. (B and C) Recombinant mouse IL-17 enhances mouse organoids growth as shown by representative mouse colon organoids images (B) and quantitative organoid area (C). (D) Western blot showing that mouse IL-17 increases the expression of colon stem cell markers, Ascl2 and Lgr5, in mouse colon organoids. (E) Western blot of phospho-stat3 with IL-17 (20 ng) and STAT3 inhibitor, stattic (20 μM). (F and G) Representative organoid images (F) and quantification of organoid area (G) with IL-17 and stattic. (H) Western blot of phospho-stat3 and phospho-p65 with IL-17 (20 ng) and an NF-κB inhibitor, BAY 11–7802 (5 μM). (I and J) Representative organoid images (I) and quantificaiton of organoid area (J) with IL-17 and BAY 11–7802. Error bars denote s.d. of triplicates. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. p-value was calculated based on Student’s t-test. .