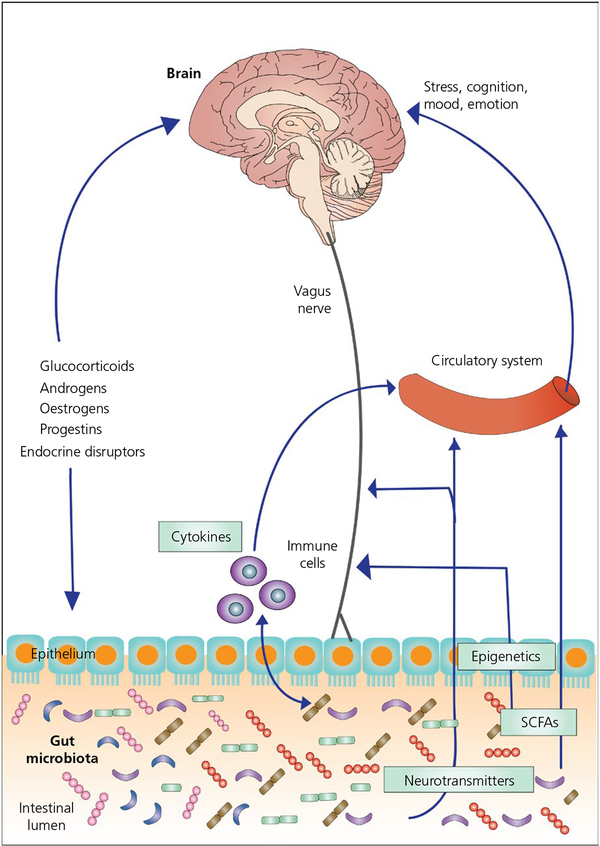
FIGURE 1.
The gut microbiome-brain axis. The gut microbiome (which consists of the microbiota, their genomes and their products) can influence brain function through a variety of mechanisms, including the production of neurotransmitters and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), the modulation of the release of cytokines by immune cells and the vagus nerve. Conversely, the brain can influence the gut microbiota via regulation of endocrine systems (eg, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axes)