Fig. 1. Bis(dipyrrinato)zinc(II) coordination polymers and mononuclear complexes.
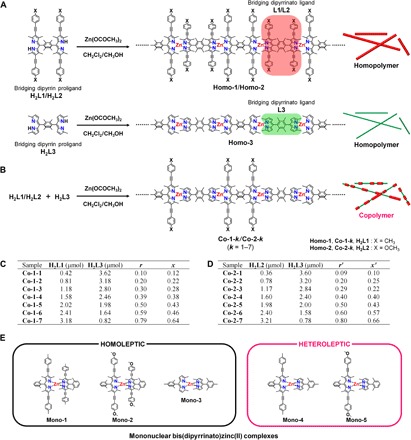
(A and B) Synthetic schemes and chemical structures of (A) homopolymers Homo-1 to Homo-3 and (B) copolymers Co-1-k and Co-2-k (k = 1 to 7). Chemical structures of constitutive bridging dipyrrin proligands (H2L1, H2L2, and H2L3) and bridging dipyrrin ligands (L1, L2, and L3) are also provided. (C) Moles of proligands H2L1 and H2L3 used to prepare Co-1-k are listed. r and x denote the mixing ratio of H2L1 to (H2L1 + H2L3) and actual mole fraction of L1 in Co-1-k, respectively. (D) Moles of proligands H2L2 and H2L3 used to prepare Co-2-k are listed. r′ and x′ denote the mixing ratio of H2L2 to (H2L2 + H2L3) and actual mole fraction of L2 in Co-2-k, respectively. (E) Chemical structures of mononuclear complexes Mono-1 to Mono-5. The heteroleptic complexes (Mono-4 and Mono-5) show brighter fluorescence than the homoleptic ones (Mono-1 to Mono-3).
