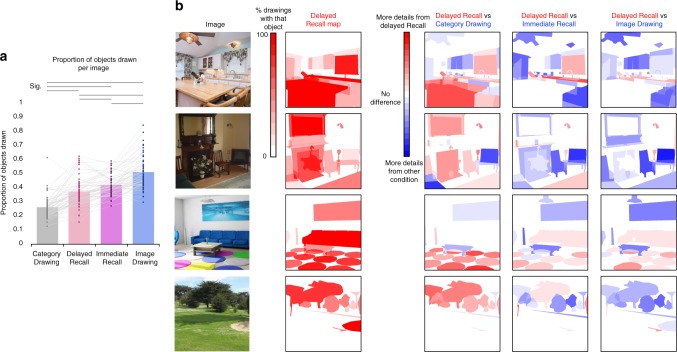
Fig. 2.
Comparison of objects drawn across conditions. a Average proportion of objects drawn for each drawing condition (Category Drawing, Delayed Recall, Immediate Recall, Image Drawing). Dots indicate average proportion for each of the 60 images used in the experiment, with lines connecting the same image across conditions. Horizontal lines above the graph indicate significant pairwise Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparisons that pass a Bonferroni-corrected significance level of p < 0.0083. b Example heatmaps of which objects were remembered. The “Delayed Recall Map” shows the drawing frequency of each object in the Delayed Recall drawings. Bright red indicates objects remembered by all participants who drew the image, and white indicates objects that were not remembered by anyone (white also indicates the background). The heatmaps on the right indicate the difference between the Delayed Recall heatmap (red) and the corresponding heatmaps for Category Drawing, Immediate Recall, and Image Drawing (blue), where white is a neutral color (background and objects that were drawn with equal frequency in both conditions). There were generally more objects in Image Drawings and Immediate Recall than the Delayed Recall drawings (e.g., more blue in the “Delayed Recall vs Image Drawing”), but there were also several objects participants remembered equally well (e.g., the flowers in the living room, the table in the kitchen), or even drew more frequently from memory than when perceiving the image (e.g., the hoe in the golf scene, the chef in the middle of the kitchen table). Image Drawings and Immediate Recall also show extremely similar heatmaps, showing the objects recalled immediately after encoding are much like those drawn at perception. The “Delayed Recall vs Category Drawing” heatmaps show that Delayed Recall drawings contained several items beyond what would exist in a canonical image from that scene category (e.g., circular rugs in a living room, a table in a kitchen), but there are also some objects that would be canonically drawn but participants did not successfully recall (e.g., the television in the living room with the fireplace, cupboards in a kitchen)