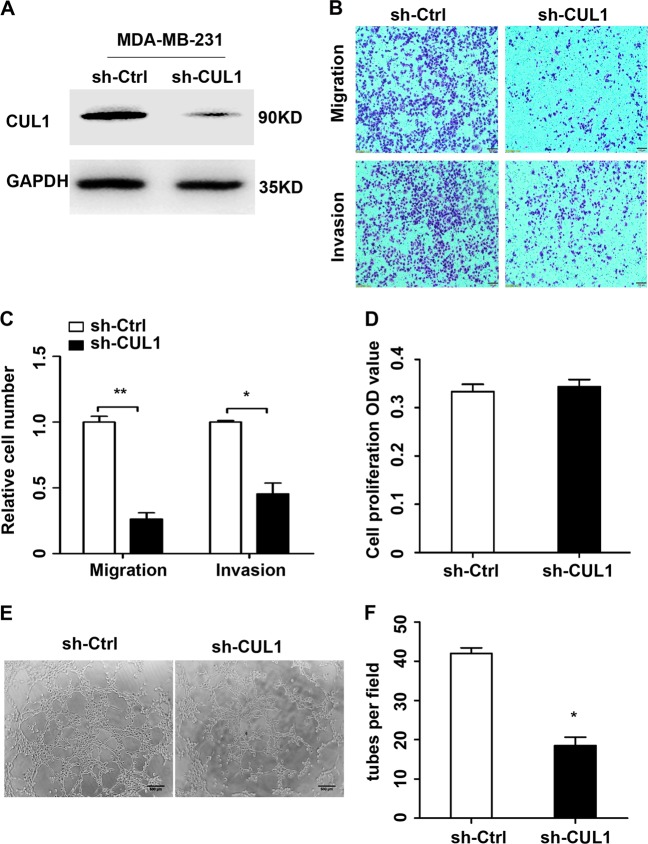
Fig. 2. CUL1 knockdown inhibited breast cancer cell migration, invasion, and tube formation in vitro.
a Lentivirus containing CUL1 knockdown (sh-CUL1) and vector control (sh-Ctrl) plasmids were used to infect MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. b The migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells with CUL1 knockdown and vector control. c The number of cell migration and invasion per field was counted in five random fields (n = 3/group). d The HUVECs cell proliferation absorbance (OD) value in the conditioned medium collected from MDA-MB-231 cells with CUL1 knockdown and vector control. e The tube formation by HUVECs in the conditioned medium collected from MDA-MB-231 cells with CUL1 knockdown and vector control. f The number of tubes formed per field was counted in five random fields (n = 3/group). Data were presented as mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test)