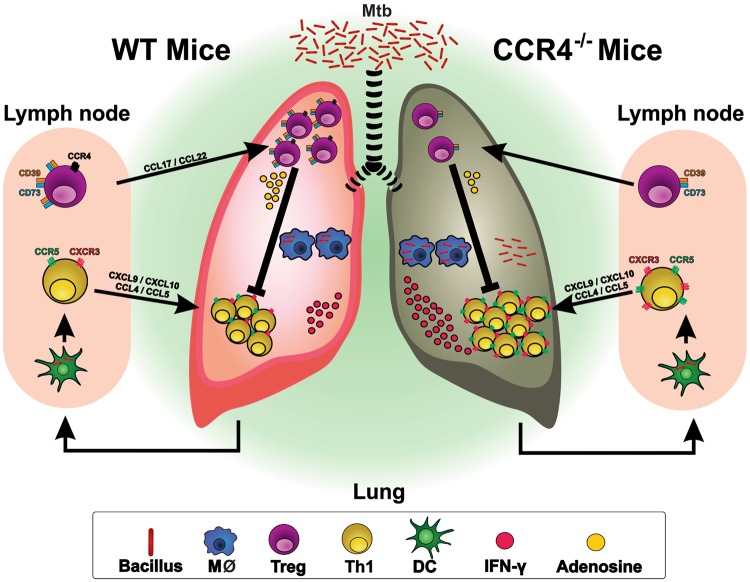
Fig. 7. Proposed model of collected findings.
CCR4 regulates the magnitude of pulmonary inflammation at the chronic phase of M. tuberculosis infection by a mechanism dependent on the balance in the ratio of CD4+Foxp3+regulatory T cells and CD4+ Th1 effector cells, as well as in the suppressor function of regulatory T cells. Consequently, CCR4 deficiency accentuates the susceptibility to infection by a mechanism dependent on exacerbated magnitude of Th1 cell-mediated pulmonary inflammation