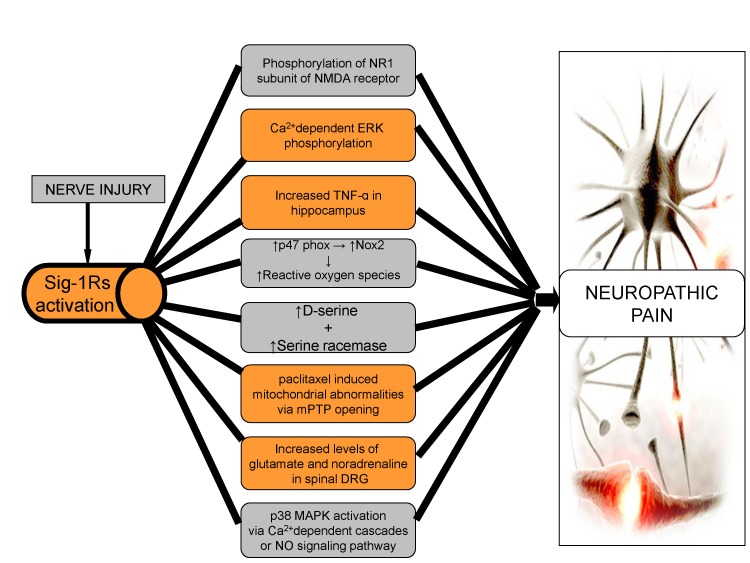
Fig. 2. Role of sigma receptors in neuropathic pain.
After nerve injury, there is activation of Sig-1Rs, with an increase the intracellular entry of Ca2+, resulting in increased phosphorylation of NMDA, ERK, p38 MAPK and activation of NO signaling leading to neuropathic pain. Increased levels of D-serine, glutamate and nor-adrenaline along with mitochondrial abnormalities via Sig-1Rs are major factors in the induction of neuropathic pain. Production of reactive oxygen species through Nox2 and TNF-alpha, via Sig-1Rs may also contribute to neuropathic pain.