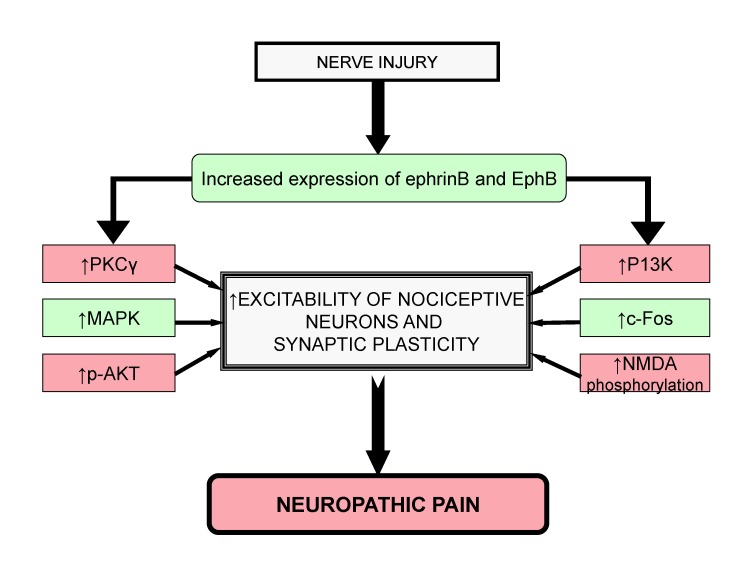
Fig. 3. Role of Ephrins and EphB receptor tyrosine kinase leads in neuropathic pain.
After nerve injury, the increased levels of PKCγ, MAPK, c-Fos, p-AKT, P13K and NMDA phosphorylation through ephrinB and EphB signaling lead to increased excitability of nociceptive neurons and synaptic plasticity that contributes to neuropathic pain.