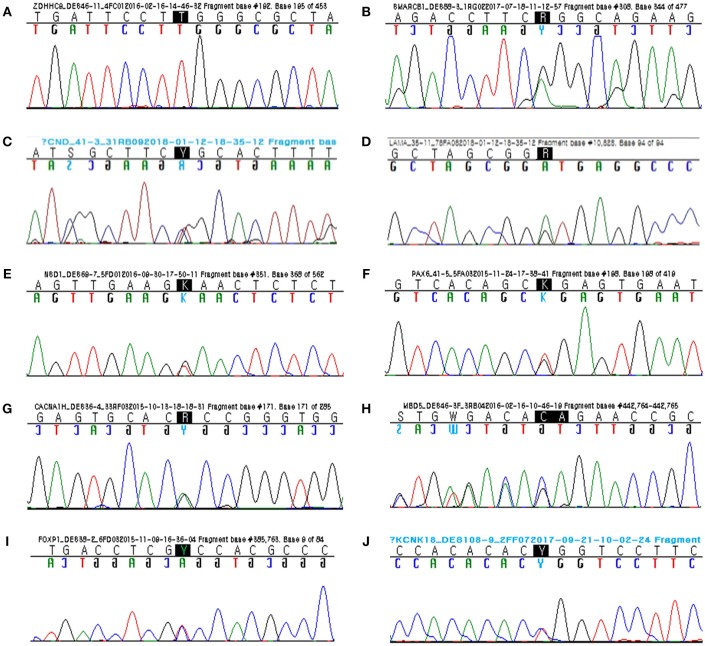
Figure 1.
Sanger sequencing confirmed segregation of the rare variants related to the disease phenotypes. (A) Hemizygous missense mutation (c.286C>T; p.Arg96Trp) of ZDHHC9. (B) Heterozygous missense mutation (c.31G>A; p.Gly11Arg) of SMARCB1. (C) Heterozygous missense mutation (c.4651C>T; p.Arg1551Cys) of CHD8. (D) Heterozygous donor splice site mutation (c.10828+1G>A) of LAMA5. (E) Heterozygous nonsense mutation (c.1789G>T; p.Glu866*) of NSD1. (F) Heterozygous nonsense mutation (c.19G>T; p.Gly7*) of PAX6. (G) Heterozygous missense mutation (c.5675G>A; p.Arg1892His) of CACNA1H. (H) Heterozygous frameshift mutation (c.254_255delGA; p.Arg85Asnfs*6) of MBD5 (reverse). (I) Heterozygous missense mutation (c.155C>T; p.Ala52Val) of FOXP1. (J) Heterozygous missense mutation (c.301T>C; p.Trp101Arg) of KCNK18.