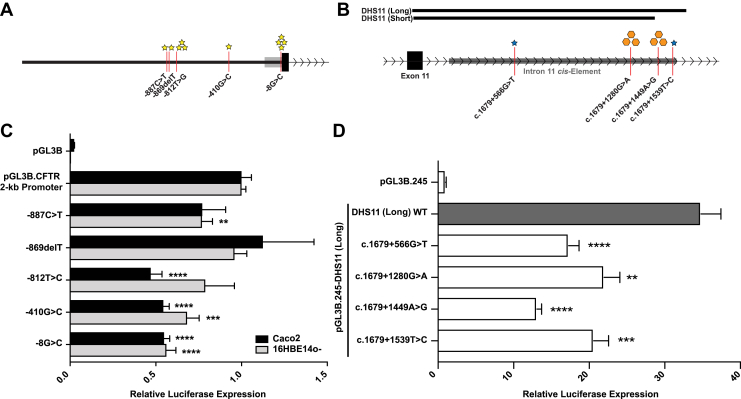
Figure 2.
Promoter variants reduce activity of 2-kb CFTR promoter in a cell type–independent manner. A and B: Schematic of five variants identified within the 2-kb CFTR promoter (A) and four substitutions identified within the CFTR intron 11 cis-element (B). Stars represent individual patients with observed variant (blue, homozygous variant; yellow, heterozygous variant), and orange hexagons represent 10 patients heterozygous for the observed variant. C: Luciferase expression vectors containing the 2-kb CFTR promoter [wild type (WT) or with variants] were transiently cotransfected into 16HBE14o- or Caco2 cells. Data are shown relative to the CFTR 2-kb promoter parental vector. pGL3B, lacking a promoter, is shown for control. D: Luciferase expression vectors containing the 787-bp minimal CFTR promoter and the DHS11 long (WT or with variants) cis-element were transiently cotransfected into Caco2 cells. Data are shown relative to the CFTR minimal promoter parental vector (pGL3B.245). C and D: Luciferase expression levels were compared against pGL3B.2 kb (C) and pGL3B.245-DHS11(long) (D) using unpaired t-tests. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (C and D). n = 12 (C); n = 9 (D). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 versus pGL3B.2 kb (C; unpaired t-test) and versus pGL3B.245-DHS11(long) (D; unpaired t-test). DHS, DNaseI hypersensitive site.