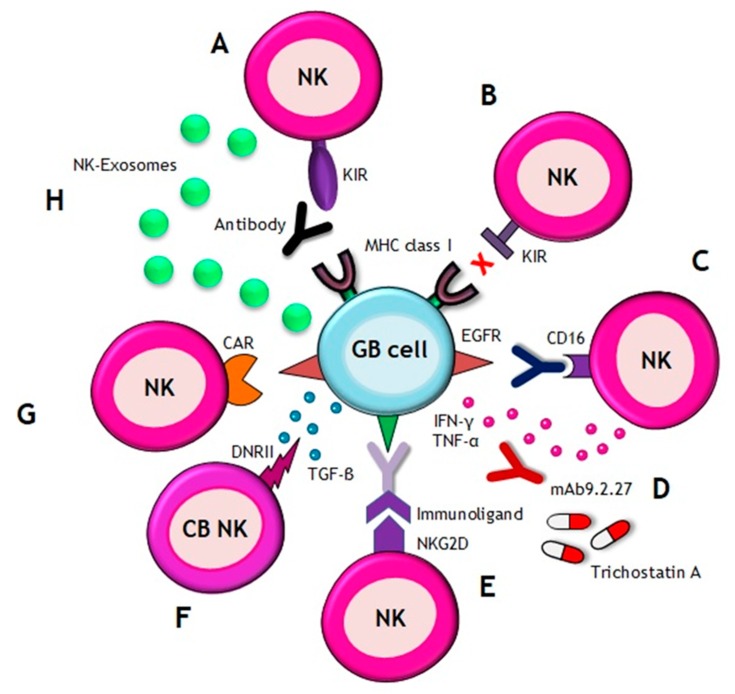
Figure 2.
Natural Killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapy. There are different approaches of immunotherapy in GB, including (A) the use of the antibodies which inhibit the interaction between KIRs on NK cells and MHC class I on GB cells, (B) transference of allogenic NK cells that express different KIRs and, thus, they are notable to recognize MHC class I on GB cells, (C) the use of antibodies against EGFR, which are recognized by CD16 receptor of NK cells, (D) combination of NK cells with the following: drugs, such as trichostatin A, for sensitizing GB cells to the NK attack; or with mAb9.2.27 antibody for inhibiting angiogenesis by secretion of IFN-γ and TNF-α, (E) the use of immunoligands conjugated to a NKG2D receptor on NK cells, which have the ability to recognize tumor-specific antigens, (F) the use of cord blood (CB) NK cells expressing a dominant negative TGF-β receptor II (DNRII) which allow NK cells being activated even in presence of TGF-β, (G) the use of NK cell line carrying a CAR targeting EGFR variant III (expressed in tumors) for inducing apoptosis and (H) the utilization of NKs-derived exosomes which promote apoptosis.