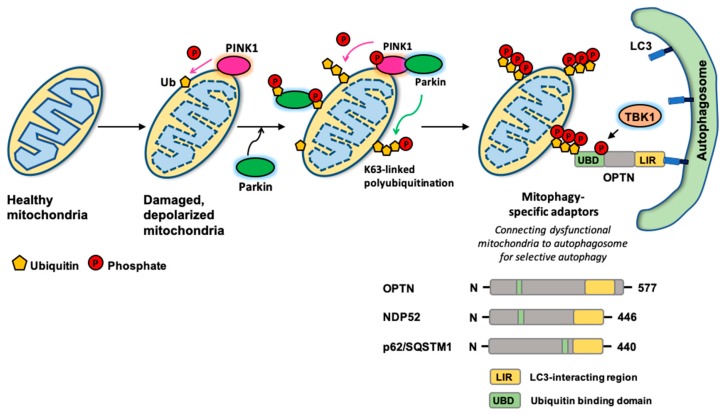
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram of the selective autophagy for mitochondria, PINK1-Parkin dependent mitophagy. As a central place dictating cell survival and death, the clearance of damaged mitochondria by autophagy (mitophagy) is particularly important. Here, the PINK1-Parkin mediated ubiquitin-dependent pathway is introduced. In response to mitochondrial damage by depolarizing mitochondrial potential, PINK1 is no longer processed by a set of mitochondrial protease systems, and PINK1 is stabilized to accumulate on the mitochondria. And then, PINK1 recruits and activates Parkin by phosphorylating both ubiquitin and Parkin. Activated Parkin on mitochondria poly-ubiquitinates (mostly, Lys63-linked chain) myriad proteins on the damaged mitochondria. Mitophagy adaptors such as OPTN, NDP52, and p62/SQSTM1 function as a bridge between these poly-ubiquitin chains on the damaged mitochondria (via their UBD domain) and LC3 on the autophagosome (via their LIR motif). TBK1 is a protein kinase activated by mitochondrial damage, and phosphorylates the mitophagy adaptor OPTN to increase the binding affinity between OPTN and poly-ubiquitin chains on the dysfunctional mitochondria, thereby, accelerating mitophagy.