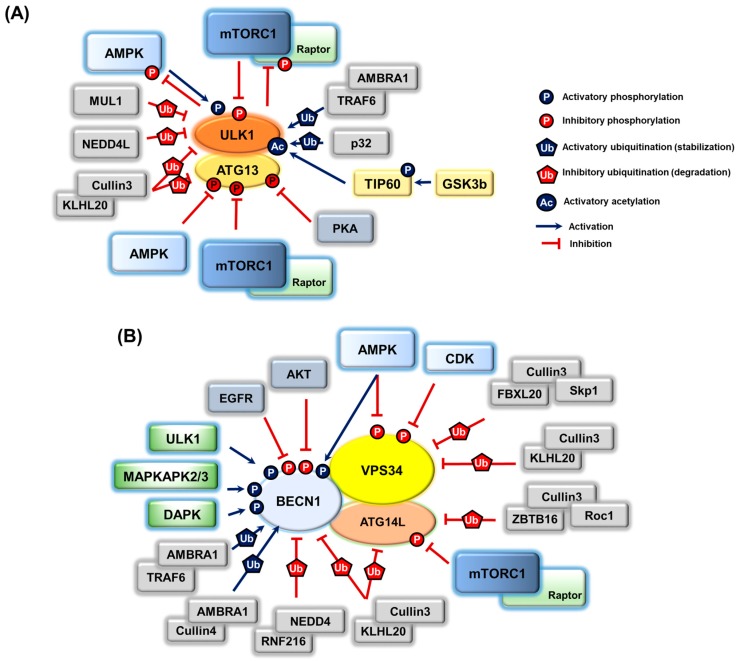
Figure 3.
Post-translational modifications and regulations of two key autophagy-initiating kinase complexes, the ULK1 and PIK3C3/VPS34 complex. (A) The ULK1 complex is regulated by phosphorylation and is activated by multiple phosphorylations on a catalytic subunit ULK1 by AMPK, and inhibited by phosphorylation on ULK1 (mTORC) as well as ATG13 (mTORC1, PKA, and AMPK). Additionally, the ULK1 complex is activated by ubiquitination on ULK1 (AMBRA1-TRAF6 and p32), whereas it is negatively regulated by ubiquitination-dependent degradation (ULK1 by MUL1, NEDD4L, and Cullin3-KLHL20, ATG13 by Cullin3-KLHL20). In response to growth factor depletion, acetylation of ULK1 is increased by the activated GSK3-TIP60 acetyltransferase axis, resulting in autophagy induction. ULK1 may constitute a negative feedback loop to its upstream regulators, AMPK and mTORC1, by phosphorylating the mTORC1 subunit Raptor protein and all AMPK complex subunits. (B) Phosphoregulation of the PIK3C3/VPS34 complex is observed in the catalytic subunit VPS34 lipid kinase (AMPK and CDK for inhibition), BECN1 (AMPK, ULK1, MAPKAPK2/3, and DAPK for activation; AKT/PKB and EGFR for inhibition), ATG14L/Barkor (mTORC1 for inhibition), and UVRAG (mTORC1 for inhibition). Ubiquitinations on VPS34 (FBXL20-Skp1-Cullin1 and Cullin3-KLHL20 for degradation), BECN1 (NEDD4-RNF216 and Cullin3-KLHL20 for degradation, AMBRA1-TRAF6 or Cullin4 for stabilization), and ATG14L/Barkor (ZBTB16-Cullin3-Roc1 and Cullin3-KLHL20 for degradation) are also important for autophagy regulation.