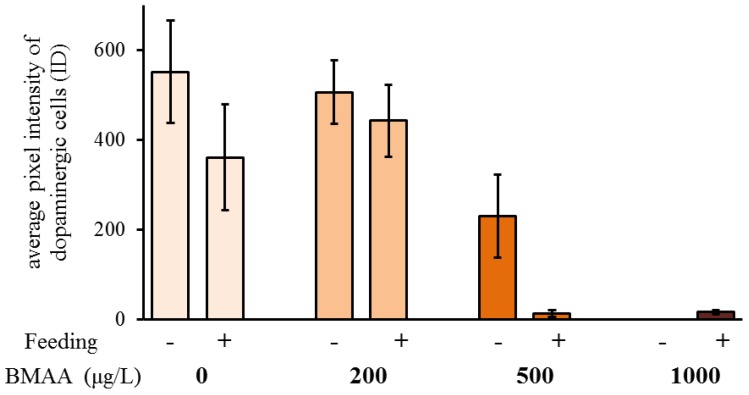
Figure 8.
Beta-methyl-amino-l-alanine (BMAA) decreases immunofluorescence of the dopaminergic neurons, measured as integrated density (ID = fluorescent area of the dopaminergic neurons × their average pixel intensity). Both feeding state and BMAA treatment have a significant effect on the immunofluorescence of the dopaminergic neurons (two-way ANOVA, feeding state: p < 0.05, BMAA: p < 0.0001, feeding state × BMAA: p > 0.05). Sample size for the non-feeding females: 0 µg L−1 BMAA n = 16; 200 µg L−1 BMAA n = 10; 500 µg L−1 BMAA n = 13; 1000 µg L−1 BMAA n = 14. Sample size for the feeding females: 0 µg L−1 BMAA n = 14; 200 µg L−1 BMAA n = 11; 500 µg L−1 BMAA n = 17; 1000 µg L−1 BMAA n = 16. Error bars represent SEM.