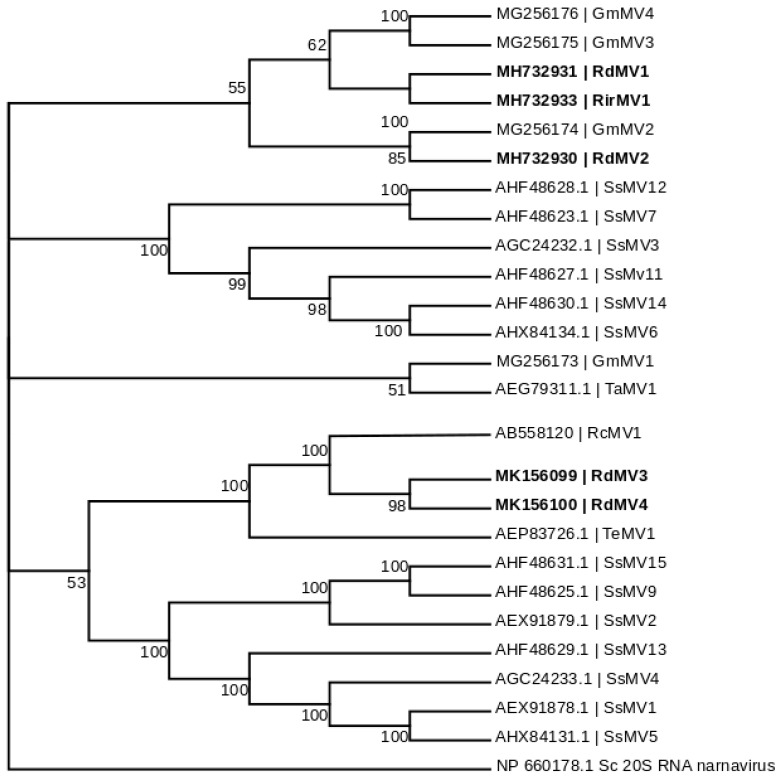
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood tree (with bootstrap consensus) depicting the relationships of the predicted amino acid sequences of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of the Rhizophagus mitoviruses, and other confirmed and proposed members of the Narnaviridae. Predicted RdRp amino acid sequences were aligned with ClustalW [31], and the phylogenetic tree was inferred using Mega 7.0 software [32]. Branch lengths are scaled to the expected underlying number of amino acid substitutions per site. The Saccharomyces 20S RNA narnavirus RdRp amino acid sequence was used as an outgroup to root the tree. Five newly identified mitoviruses (in bold) formed two separate monophyletic clusters between the Rhizophagus-associated mitoviruses. The following abbreviations were used for the Mitovirus (MV) sequences: Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Gm, Gigaspora margarita; Rd, Rhizophagus diaphanum; Rc, Rhizophagus clarus; Sc, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum; Rir, Rhizophagus irregularis; Ta, Tuber aestivum; Te, Tuber excavatum.