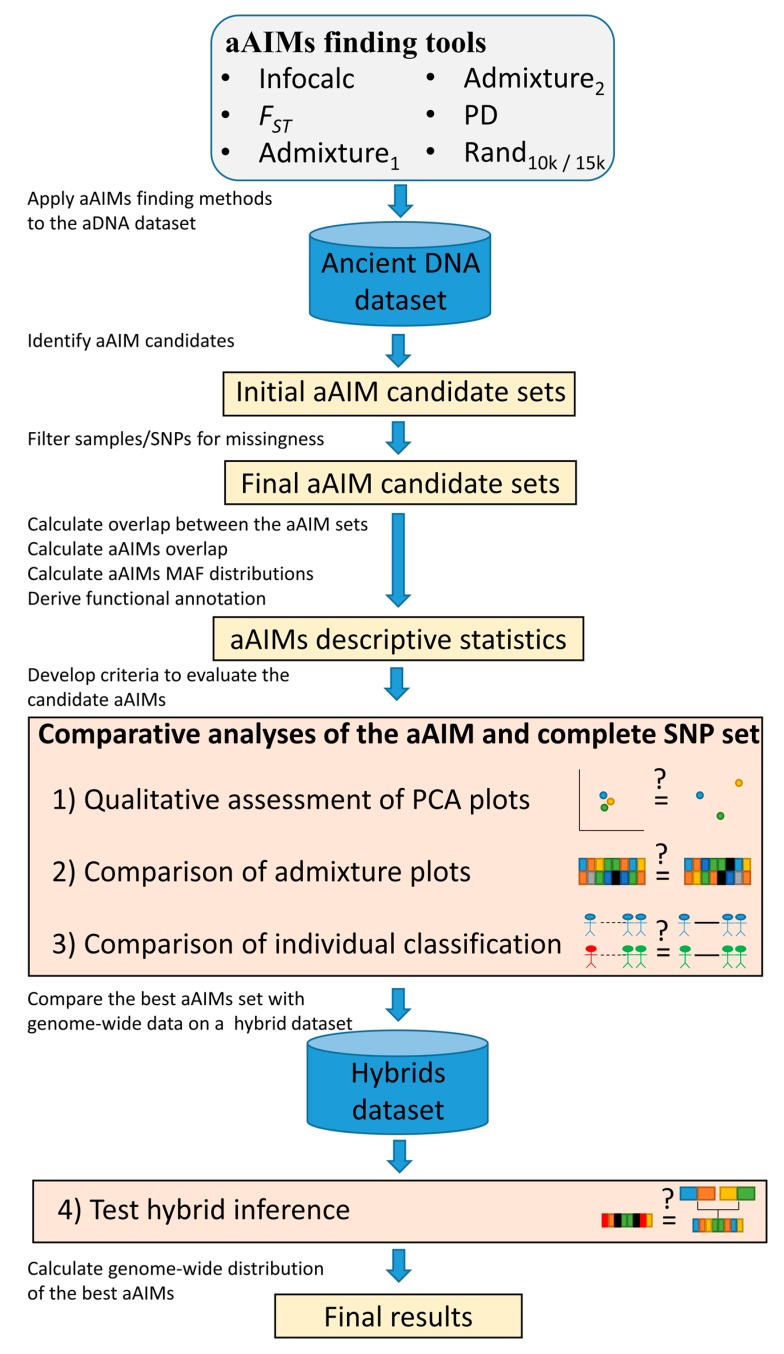
Figure 2.
A workflow to identify and evaluate the accuracy of ancient ancestry informative markers (aAIM)-finding algorithms compared to each other as well as to the complete single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (CSS) set. We adopted four criteria to evaluate how well the aAIM candidates captured the population structure depicted by the CSS. First, we qualitatively compared the dispersal of genomes obtained from a principal component analysis (PCA) to that of the CSS. Second, we compared the Euclidean distances between the admixture proportions of each genome and those obtained from the CSS. To avoid inconsistencies between the SNP sets, we used admixture components obtained through a supervised ADMIXTURE (see methods). Third, we tested which aAIMs classified individuals to populations most accurately. Finally, we evaluated the ability of the top performing method to identify admixed individuals against the CSS. aDNA: ancient DNA.