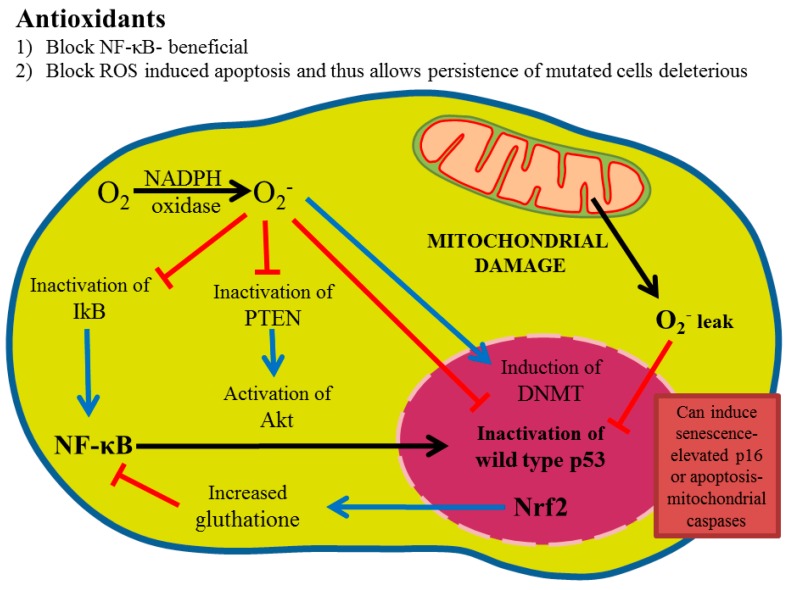
Figure 1.
Overview of reactive oxygen signaling. Superoxide, which can arise from NADPH oxidases action or mitochondrial leak, oxidatively inactivate p53, PTEN, and IkB, leading to Akt and NF-κB activation. Reactive oxygen inhibition with NADPH oxidase inhibitors can reverse this phenotype. Glutathione formation through Nrf2 activation can lead to reactive oxygen reduction and, thus, possibly an NF-κB decrease but also may react with chemotherapy and radiation generated species, thus, protecting tumor cells.