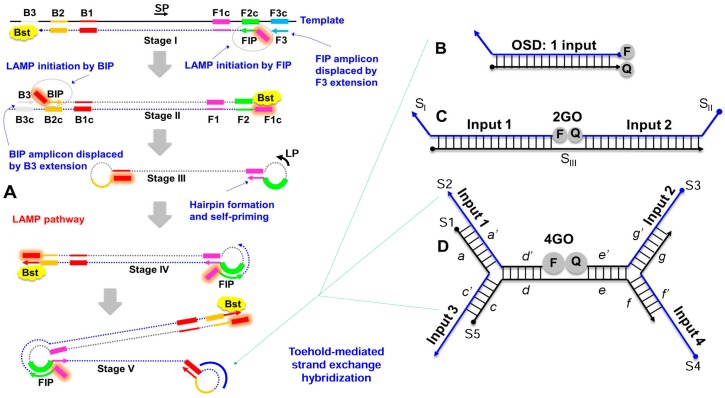
Figure 1.
Schematic depicting (A) loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) integrated with (B) one-, (C) two-, or (D) four-input oligonucleotide strand exchange signal transducers. LAMP uses 2 inner (FIP and BIP) and 2 outer (F3 and B3) primers along with the optional stem (SP) and loop (LP) primers to prime strand displacement DNA amplification by Bst DNA polymerase. The resulting continuous amplification (initiated by both new primer-binding and by self-priming) generates double-stranded concatameric amplicons containing single-stranded loops to which non-priming oligonucleotide strand exchange signal transducers can hybridize. The one-input OSD signal transducer composed of one long and one short DNA strand can hybridize to a single LAMP amplicon loop sequence leading to separation of the fluorophore (F) and quencher (Q). The OR Boolean logic processing two-input strand exchange transducer, 2GO, is composed of two labeled strands, SI and SII, and a third bridging strand SIII. Either SI and/or SII can hybridize to their specific LAMP loop sequences resulting in separation of F and Q. The four-input 4GO probe composed of 5 DNA strands (S1–S5) can hybridize to any combination of up to four different LAMP amplicon loops and perform an OR Boolean operation to produce fluorescence signal. The 4GO probe is denoted in terms of lettered domains (a–g), each of which represents a short fragment of DNA sequence in an otherwise continuous oligonucleotide strand. Complementarity is denoted by a single prime symbol.