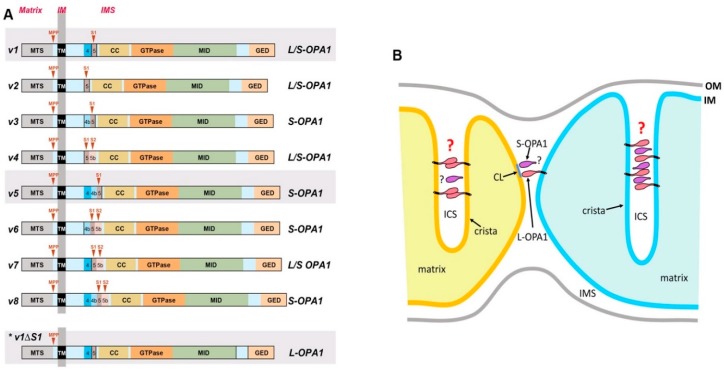
Figure 3.
OPA1 variants and operating models for IM fusion and cristae width maintenance. (A) Eight different OPA1 variants. Cleavages at S1 and S2 generate S-OPA1. OPA1-v3, v5, v6, v8, which contain the region encoded by exon 4b, are cleaved completely to generate only S-OPA1. The cleavage in the other four variants is incomplete, generating both L- and S-OPA1 (L/S-OPA1). OPA1-v1∆S1 (*) is an experimentally generated mutant in which the S1 site is deleted in the OPA1-v1 variant, and thus forms only L-OPA1. OPA1-v1, v5, and v1∆S1 (shaded) were used as representatives for L/S-, S-, and L-OPA1, respectively, in our study [96]. MPP, mitochondrial processing peptidase. (B) IM anchored L-OPA1 binds to CL of opposing IM for tethering and subsequent fusion, and S-OPA1 may facilitate this process. Cristae tightness may be maintained by trans-interaction of L-OPA1 (left crista) or by L-OPA1 oligomerization that is facilitated by S-OPA1 functioning as molecular staples (right crista). However, these models have recently been challenged by a new finding that S-OPA1 can maintain cristae tightness.