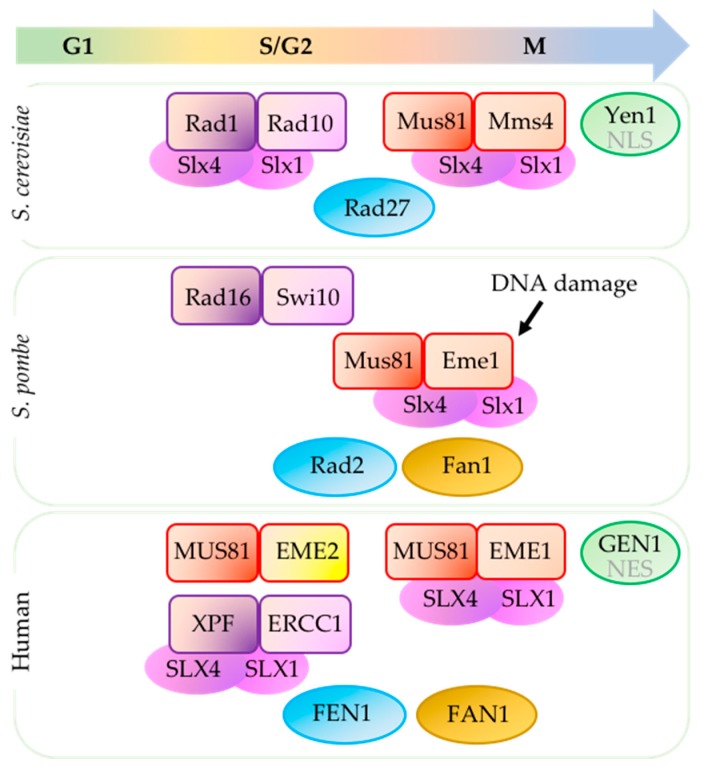
Figure 1.
Structure-specific endonucleases (SSEs) in different phases of the cell cycle. Mus81 (methyl methane sulfonate (MMS) and UV-sensitive protein 81) activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human cells is stimulated during G2-M transition (reviewed in [8]). In Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Mus81 is activated by DNA damage. Xeroderma pigmentosum group F complementing protein (XPF)-excision repair cross-complementing group 1 (ERCC1) (orthologs Rad1-Rad10S.c. and Rad16-Swi10S.p.) is important for various DNA repair pathways and cleaves replication intermediates during S and G2 phases [10]. Scaffold protein SLX4 with associating partner SLX1 interacts with MUS81-EME1 (essential meiotic endonuclease 1) and XPF-ERCC1 in human cells (reviewed in [11]) [12,13,14,15] and their orthologs in in S. cerevisiae (reviewed in [16]) [17,18,19,20]. In contrast, Slx4 does not affect Rad16-Swi10 in S. pombe [21]. Activity of Yen1S.c. is prevented until anaphase by restricting its nuclear entry due to phosphorylation of nuclear localization signal (NLS) [22,23,24]. Due to nuclear export signal (NES), GEN1 in human cells is able to access chromosomes only after nuclear membrane breakdown during mitosis [25]. S. pombe do not have Yen1 ortholog (reviewed in [26]). FEN1 (flap endonuclease 1) (orthologs Rad27S.c. and Rad2S.p.) and FAN1 (Fanconi-associated nuclease I) (missing in S. cerevisiae) contribute to processing replication intermediates but cell cycle-dependent regulation of these SSEs are not well characterized (reviewed in [8]). Mms4 (methyl methane sulfonate sensitivity protein 4).