Figure 2.
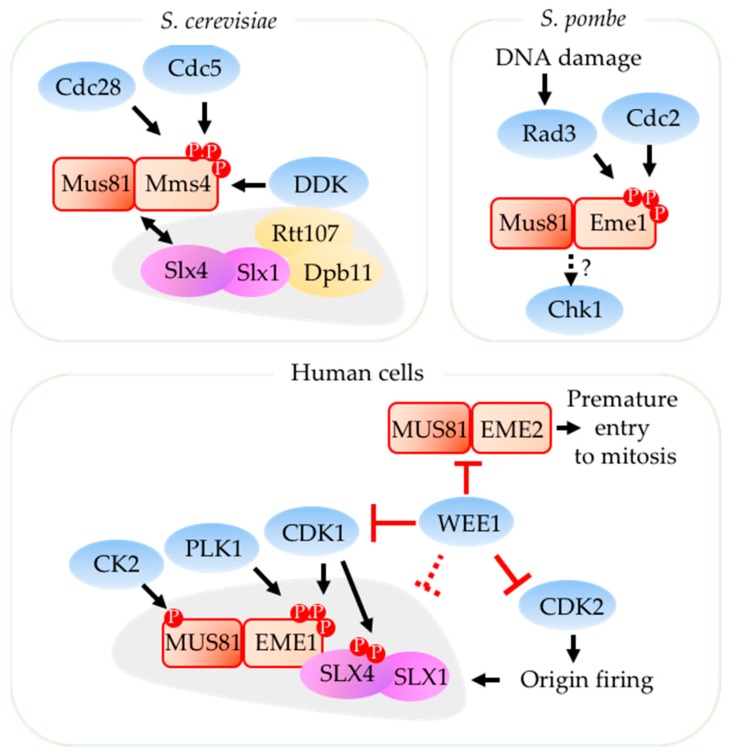
Mus81 regulation by cell cycle kinases. In S. cerevisiae, Mus81-Mms4 is phosphorylated by Cdc28S.c. (CDK1 ortholog) and Cdc5S.c. (PLK ortholog) kinases at the G2/M transition [48,49,50]. Scaffold protein Rtt107S.c. (PTIP ortholog) associates with Dpb11S.c. (TOPBP1 ortholog) and interacts with DDK which also phosphorylates Mms4S.c. [52]. Rtt107-Dpb11-Slx4S.c. complex associates with Mus81-Mms4S.c. behind replication forks. In S. pombe, Mus81-Eme1S.p. is phosphorylated by Cdc2S.p. (CDK1 ortholog) which primes Eme1S.p. for phosphorylation by Rad3S.p. (ATR ortholog) upon DNA damage [53]. Mus81-Eme1S.p. may be contributing to Chk1 activation in fission yeast as Mus81-deleted cells with replication defect are able to bypass Chk1 checkpoint [54]. In human cells, MUS81-EME1 activity peak during M phase after EME1 is phosphorylated by CDK1, PLK1 [12,58,59]. SLX4 phosphorylation by CDK1 and MUS81 phosphorylation by CK2 also promotes MUS81-EME1 activity [60]. During S-phase, WEE1 downregulates MUS81-EME1 activity by inhibiting CDK1 and thereby limiting EME1 and SLX4 phosphorylation (reviewed in [56]). WEE1 inhibition of CDK2 reduces origin firing and subsequently the replication intermediate substrates of MUS81. WEE1 may also inhibit MUS81 directly [61]. Residual MUS81 activity during S-phase comes from MUS81 that forms complex with EME2 which can promote premature entry to mitosis upon WEE1 inhibition [62].