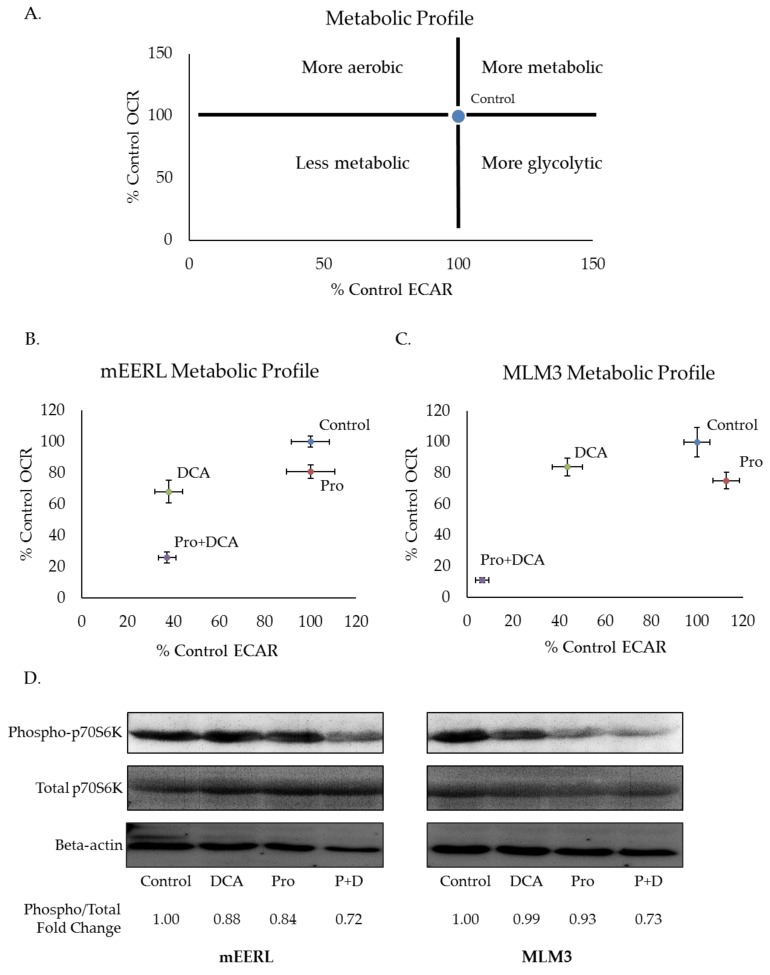
Figure 3.
Propranolol synergizes with the glycolytic inhibitor dichloroacetate (DCA) to dramatically attenuate tumor cell metabolism and mTOR signaling. Metabolic profile schematic (A), representing possible shifts in metabolic phenotype compared to control. Metabolic profiles of mEERL (B) and MLM3 cells (C) treated overnight with propranolol (40 µM) and/or DCA (10 mM). Values reflect the average of n = 3–5 independent biological replicates +/− SEM. Values were adjusted for non-glycolytic acidification and normalized to total protein. Western blot (D) assessing mTOR activity via p70S6K phosphorylation in mEERL (left) and MLM3 cells (right) following overnight treatment with propranolol (40 µM) and/or DCA (10 mM). Spot densitometry was used to calculate fold change in phosphorylated/total p70S6K signal intensity relative to control for each cell line.