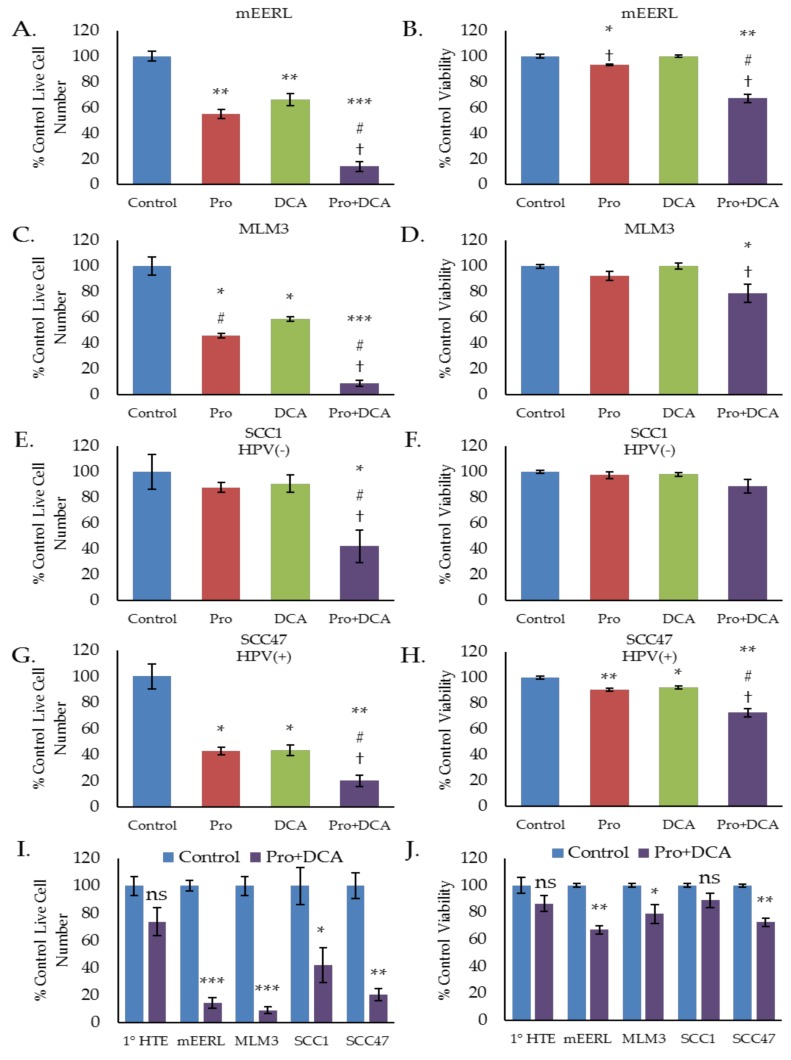
Figure 4.
The combination of propranolol and DCA synergizes for robust anti-cancer activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), but has little effect on primary tonsil epithelial cells. Cell counting (A,C,E,G,I) and trypan blue exclusion results (B,D,F,H,K) of mEERL (A,B), MLM3 (C,D), SCC1 (E,F), and SCC47 (G,H) treated with propranolol (40 µM) and/or DCA (10 mM) for 48–72 h. SCC1 and SCC47 are human papillomavirus (HPV)(−) and HPV(+) HNSCC cell lines, respectively. Comparison of Pro + DCA effects in primary human tonsil epithelial cells (1° HTE) versus HNSCC cell lines is shown in (I) and (J). Values reflects % live cell number or % viability relative to control. Each data point represents mean +/− SEM of n = 3–4 independent biological replicates; p-values reflect t-test results (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.006, *** p ≤ 0.0001 vs. control for a given cell line; # p ≤ 0.05 vs. propranolol only; † p ≤ 0.05 vs. DCA only; ns = not significant).