Figure 3.
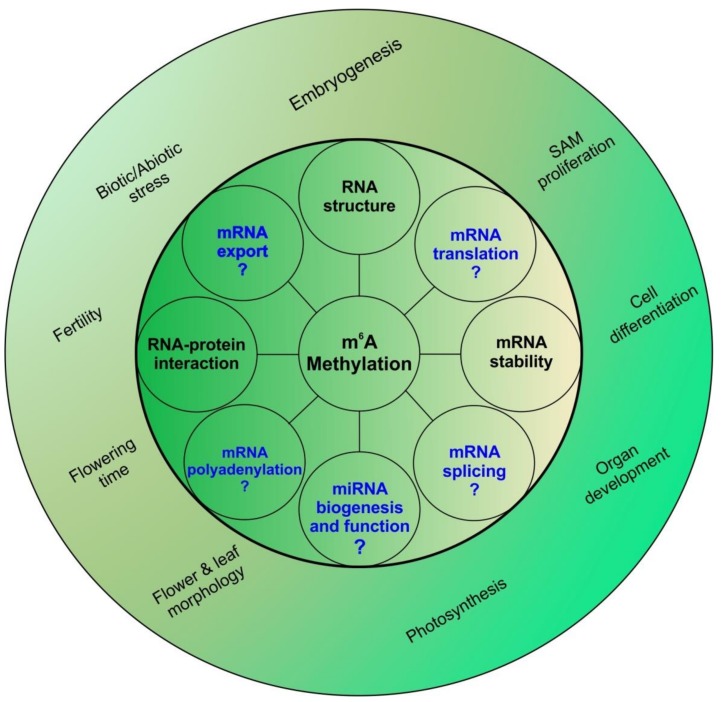
m6A and its many roles: m6A methylation has been known to alter mRNA stability and structure along with altering RNA-protein interactions at the molecular level. These changes in molecular levels are translated to a large array of physiological changes ranging from photosynthesis to stress response. In animal systems, m6A has also been shown to affect mRNA splicing, export, polyadenylation and translation; whether these also play a role in plants remains to be understood. m6A has been shown to be vital for proper shoot apical meristem (SAM) proliferation and organ development. Flower growth, morphology and fertility are also affected by m6A. In animals m6A has also been associated with microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis; whether this is true for plants is still unknown.