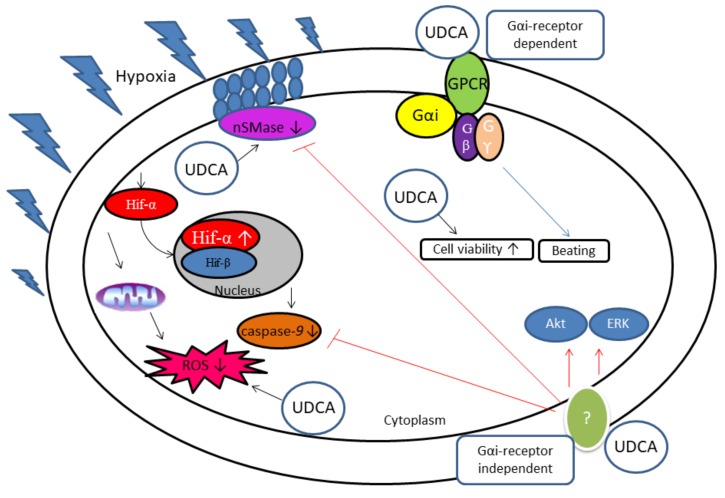
Figure 2.
Proposed anti-apoptosis mechanism for UDCA cardioprotection against hypoxia. Pertussis toxin does not block the effect of UDCA on caspase-9, neutral SMase expression, ROS production, and Hif-1α expression in hypoxia-induced CMs. Beating rate is partially inhibited by PTX, suggestive of nonsensitive PTX pathway (pathways independent of Gαi-coupled-receptor) involvement. Ursodeoxycholic acid cardioprotection has been reported to regulate the activation of survival signaling proteins (ERK 1/2 and Akt) and neutral SMase in hypoxia-induced CMs [104]. UDCA has been shown to downregulate caspase-9 protein expression and neutral SMase activity and upregulate phosphorylation of ERK 1/2 and Akt via Gαi-independent pathways (red line) to promote cardioprotection against the effects of CoCl2. Meanwhile, UDCA has been shown to inhibit Hif-1α, ROS production, and caspase-9 protein expressions in CoCl2-induced hypoxia CMs [91]. The data also suggests that UDCA cardioprotection in CoCl2-induced hypoxia could be mediated through dependent Gαi pathways on CM beating rate (blue line). GPCR: G-protein-coupled receptor; Gαi, Gi alpha subunit is a G protein subunit that inhibits cAMP from production; Gβ, G-beta; Gγ, G-gamma; nSMase, neutral sphingomyelinase; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; Hif-α, hypoxia inducible factor alpha; Hif-ẞ, hypoxia inducible factor beta; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Akt, protein kinase B; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; PTX, pertussin toxin.